State of Play
Networks and Devices for Mobile Broadband
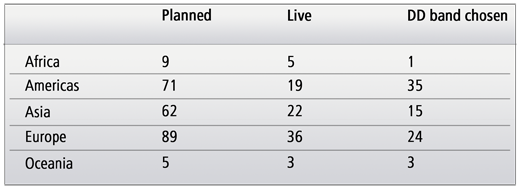
Mobile Broadband as delivered by the GSM family of technologies has been a global success. The market has grown from two deployed HSDPA networks in 2006 to over 420 by August 2012 with an additional 190 HSPA+ networks offering speeds up to 84.4Mbps (with appropriate access to spectrum). Operators are now looking to the Digital Dividend to deploy the next generation of mobile technologies, LTE, with 21 already deployed and nearly 60 planned.
LTE (FDD Only)
 Improvements in technology have gone from HSDPA offering 1.8Mbps to speeds in excess of 84Mbps peak supporting downlink data as well as standard voice.
Improvements in technology have gone from HSDPA offering 1.8Mbps to speeds in excess of 84Mbps peak supporting downlink data as well as standard voice.
This technology roadmap allows operators to have a forward looking investment path for years to come that will support data demands as they continue to increase. However, to support these higher speeds and technology enhancements as well as the growth in connections and data consumed, more spectrum will be needed by the operators.
HSPA and HSPA+ has a strong evolutionary path
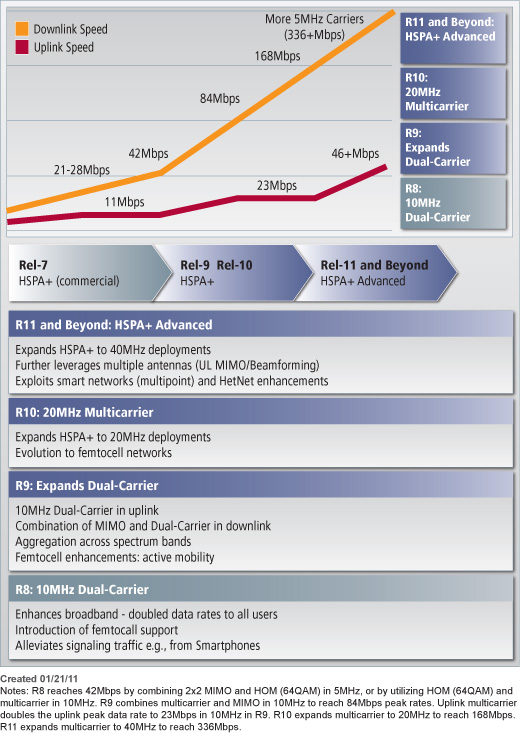
LTE Roadmap
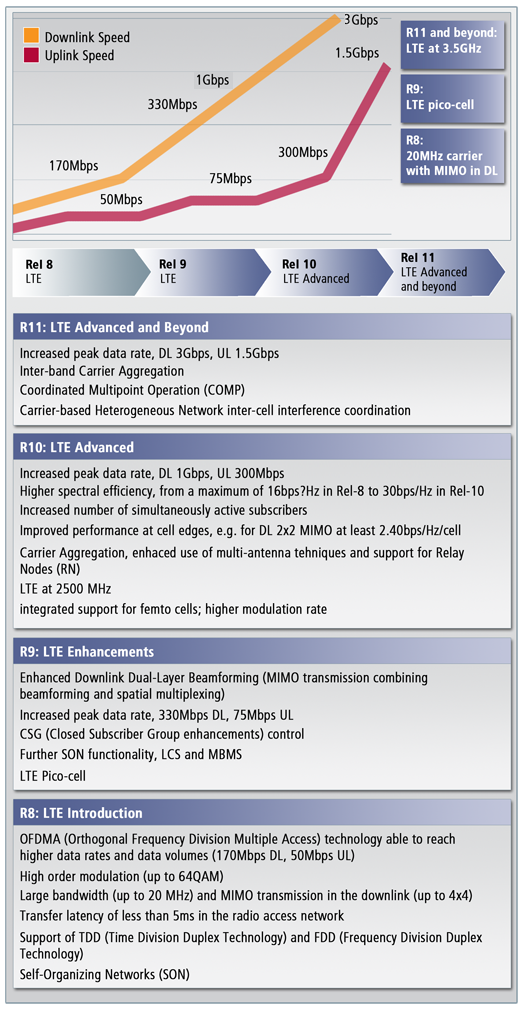 LTE has gained in popularity from all operators, not just those with GSM and HSPA but with legacy CDMA and WiMAX networks as they look to compete in their markets. There are now commercial deployments and devices coming to market from dongles to handsets, with over 400 consumer products on the market as of July 2012.
LTE has gained in popularity from all operators, not just those with GSM and HSPA but with legacy CDMA and WiMAX networks as they look to compete in their markets. There are now commercial deployments and devices coming to market from dongles to handsets, with over 400 consumer products on the market as of July 2012.
Connections
Consumer take up of Mobile Broadband services is fastest growing ever, from a mere few thousand in 2006 to over a billion connections1 in mid 2012.
WCDMA HSPA net additions (monthly)
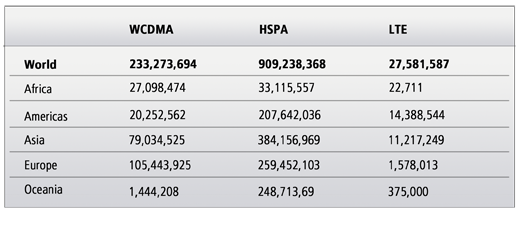
With LTE adding to these numbers, Mobile Broadband as delivered by the GSM family of technologies (including HSPA and LTE) will exceed any other form of internet access globally.


