Almost 50 years ago, Martin Cooper made the very first mobile phone call standing on the corner of 6th Avenue near the Hilton Hotel in New York City. It took a few more decades before mobile really took off, but at that moment, everything changed, and by the end of this year 5.5 billion people will be using a mobile phone.
Over the past few decades, the mobile industry has become an incredibly powerful platform. In 2021 alone, the industry contributed $4.5 trillion to the global economy, about 5% of the global GDP.
And with that comes significant responsibility.
As the world continues to face ever more complex global challenges, the mobile industry has a key role to play in bringing about change. Connecting everyone and everything to a better future.
Connectivity driving business
As 5G takes off around the world, we are starting to see its true transformational potential come to life across industries. From automotive to aviation, education to entertainment, manufacturing to the metaverse, mobile connectivity has an incredible enablement effect.
This enablement effect is also evident in low- and middle-income countries. While 5G is still in its nascent stage in many of these countries, entrepreneurs have taken full advantage of the opportunities afforded by 3G and 4G connectivity, building successful businesses, many of them addressing some of the biggest challenges facing their communities.
Recognising this, the GSMA Mobile for Development Innovation Fund was set up to support innovative digital solutions with positive socio-economic impact. To date the fund has impacted the lives of 36 million people, and generated over £563 million in additional investments for start-ups in low- and middle-income countries, helping them to scale and grow their businesses.
Mobile indusry leading the way on ESG Metrics
In 2022, the mobile industry led the way on reporting on environmental, sustainability and governance metrics, with the launch of ESG Metrics for Mobile.
Developed with EY and the Yale Center for Business and the Environment, these impact-led metrics provide a set of 10 core industry-specific and actionable KPIs structured around the four pillars of Environment, Digital Inclusion, Digital Integrity and Supply Chain.
By using the framework, operators can generate insights to support internal decision-making, communicate progress towards ESG goals, and build more trust with customers. Most importantly it demonstrated the mobile industry is committed to raising its sustainability standards, operating responsibly, and moving the dial towards a better future for us all.
Connectivity and ethical AI
Mobile big data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) are emerging as powerful forces transforming business and society, and the potential of these technologies to unlock life-changing benefits is only beginning to emerge. When grounded in ethical principles that protect privacy, these solutions can truly change the world for the better. The mobile industry is committed to the ethical use of AI in its operations and customer interactions; to protect customers and employees, remove any entrenched inequality and ensure that AI operates reliably and fairly for all stakeholders.
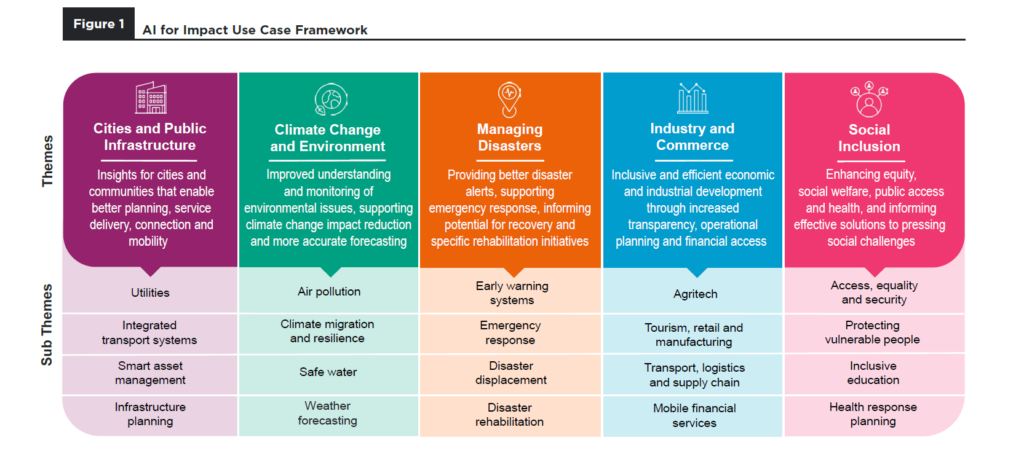
For example, during the COVID-19 crisis, Telenor provided mobility data analtyics on movement between Norway’s 356 municipalities to the Norwegian Institute of Public Health’s Covid-19 task force. Telenor’s mobility data was utilised to inform modelling of the potential spread of the virus, to develop predicted incidence in each municipality and to simulate the number of hospitalisations, intensive care patients and deaths.
Connectivity and climate action
As the impacts of climate change become obvious around the globe, the mobile industry has a key role to play in fighting the crisis.
In 2019, the mobile industry agreed to align its targets to be net zero by 2050 and was recognised as one of the first Breakthrough industries in the UN Race to Zero.
Over 80% of the global mobile industry is now disclosing climate impacts, energy and GHG emissions via the internationally recognised CDP global disclosure system. And 60% of the industry by revenue has committed to Science-Based Targets to cut their carbon emissions rapidly over the next decade.
The mobile industry also has a significant enabling effect when it comes to reducing carbon emissions in other industries. Smart technologies used in energy-intensive industries such as energy, transport, buildings and manufacturing, could enable global savings of 11 gigatonnes of carbon emissions by 2030, equivalent to roughly 40% of the total global reduction required by then, to limit global warming to 1.5oC.
The GSMA ClimateTech programme is also working to encourage greater integration between digital technology and climate mitigation, adaptation and resilience strategies in low- and middle-income countries.
Connectivity for good across the globe
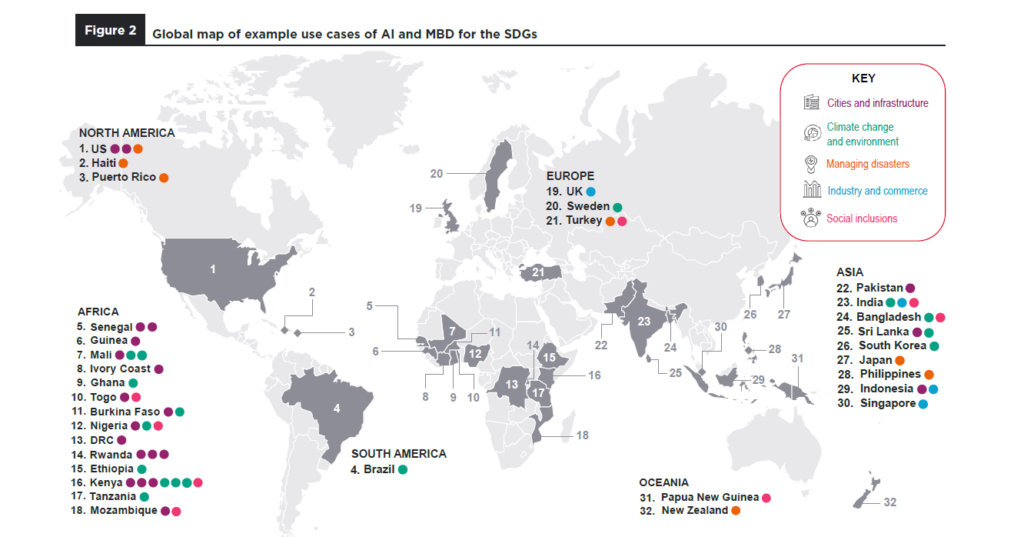
From small start-ups to large corporations, disaster management to digital inclusion, and supply chains to climate change, mobile connectivity has opened up limitless opportunities for us to do good across the world, acting as a catalyst to drive change.
Over the past two years, mobile connectivity has emerged as a steadying hand, to be relied upon and trusted in times of crisis. As the global landscape continues to evolve and present new challenges and opportunities, the mobile industry will continue to lead the way towards a better future in which people, industry and society thrive.
Find out more: www.gsma.com/connectivityforgood