The planned merger between True Corporation (“True”) and Total Access Communication (“dtac”) in Thailand is currently awaiting regulatory approval. The announcement of the merger or “amalgamation” as the involved companies like to call it, wasn’t unexpected as rumors around dtac’s owner Telenor’s plans to exit Thailand circulated for a while. Besides, Telenor hopes to merge its Malaysian operations and it sold its operations in Myanmar in March 2022. On November 20, 2021, True and dtac entered a non-binding memorandum of understanding to pursue the “amalgamation.” In April 2022, the two companies received the approval from their shareholders for the merger and to create a new listed company — NewCo — despite not knowing what the conditions or measures of the deal will be. In June 2022, a legal subcommittee of NBTC concluded that the telecom regulator has the power to approve or dissolve the planned merger. In this article we will assess the impact of the proposed merger on the Thai telecommunications market by examining its current state.
Key takeaways
- Thailand’s 5G performed well compared to its regional counterparts due to a timely 5G network roll out and dedicated 5G spectrum availability.
- Based on mobile performance, Thailand is a market dominated by one player — AIS. It had a lead in terms of 4G performance and that lead has been extended further with 5G. The third operator in the market, dtac, is not competitive on 5G due to its limited spectrum holdings (dtac’s 5G performance is equivalent to AIS’ 4G).
- The merged operator, NewCo, could provide more robust competition to AIS while also having the scale to invest in 5G. While this will turn Thailand into a two-player market, examples of mergers and acquisitions in other countries suggest a number of measures will be most likely put in place: spectrum divestment, more capacity allocated to MVNOs, converged and innovative offerings, all of which can potentially offset its negative impact.
Thailand’s 5G performs well compared to its regional counterparts
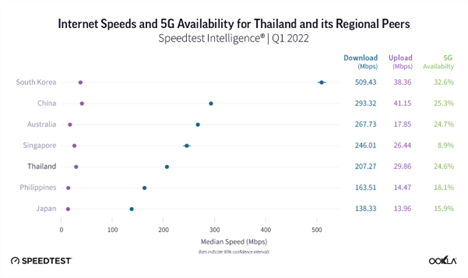
5G deployment in Thailand is comparable in terms of 5G speeds and 5G Availability with more developed countries in the region such as Singapore, even though the country previously lagged behind its peers in assigning 3G and LTE spectrum.
In our recent article, we concluded that the country’s regulator, The National Broadcasting and Telecommunications Commission (NBTC), has been instrumental in establishing Thailand as a leading 5G market in the region. In fact, Thailand was one of the first markets to launch 5G in the Asia-Pacific region, with AIS and TrueMove H both launching commercial 5G services in Q1 2020, shortly after the conclusion of the country’s 5G auction. The Thai government plays an active role in ensuring 5G can bring societal benefits, e.g., improving government services and extending healthcare access. Some of the campaigns include establishing a telemedicine center, setting up a 5G network for smart city management, developing a pilot project on digital farming in Songkhla Lake Basin, and using 5G connectivity for pandemic related measures as tourism was reopening in Phuket.
In Q1 2022, Speedtest Intelligence® data put Thailand on par with its regional peers such as Australia and China and ahead of the Philippines, Japan, Singapore and New Zealand in terms of 5G Availability (the proportion of users on 5G-capable devices who spend a majority of their time on 5G networks).
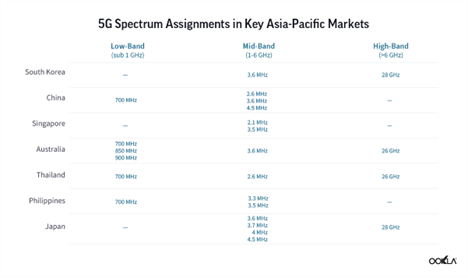
In February 2020, NBTC assigned spectrum for 5G use across low (700 MHz), mid (2,600 MHz), and high (26 GHz) frequency bands. It also plans a further auction of mid-band spectrum in 2022 in the 3.5 GHz band, which was vacated in September 2021 by Thaicom, a satellite provider. All of the countries in the comparison above assigned spectrum in the mid-band frequency, which is the sweet spot for 5G in terms of coverage and capacity. In South Korea, which came first in terms of median 5G download speed, the government allocated a total of 2,680 MHz of spectrum including 280 MHz in the 3.5 GHz band and 2,400 MHz in the 28 GHz spectrum band. Korean provider KT is also using a standalone 5G network, a form of 5G that doesn’t rely on 4G LTE as the foundation of the 5G experience, which should provide faster speeds and lower latency than non-standalone (NSA) 5G networks. In fact, a few operators in the analyzed countries have launched 5G SA including China (all operators), Singapore (M1, Singtel, and Starhub), Australia (Telstra and Vodafone), Japan (Softbank), and Thailand (AIS).
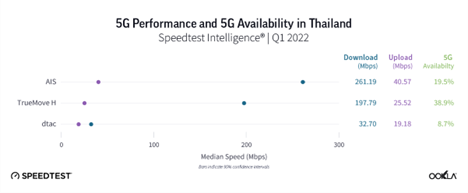
AIS wins on 5G performance in Thailand, TrueMove H on 5G Availability
In Q1 2022, AIS came as the fastest operator in terms of 5G speeds, this was also the case in Q4 2021 as per our recent article. According to Speedtest Intelligence, AIS recorded a median 5G download speed of 261.19 Mbps and 5G upload speed of 40.57 Mbps during Q1 2022. AIS launched 5G NSA (non-standalone) in February 2020 using the 700 MHz, 2.6 GHz and 26 GHz bands, followed by 5G SA in July 2020 in cooperation with Huawei. AIS deployed 5G CA (New Radio Carrier Aggregation) by integrating its mid-band (2600 MHz) and low band (700 MHz) spectrum. This in turn gave a 1.7x boost to the operator’s data transmission capabilities. TrueMove H was second for 5G download speed, with a median of 197.79 Mbps and a 5G upload speed of 25.52 Mbps. The lack of mid-band spectrum limits dtac’s performance, which showed a median 5G download speed of 32.70 Mbps and 19.18 Mbps upload.
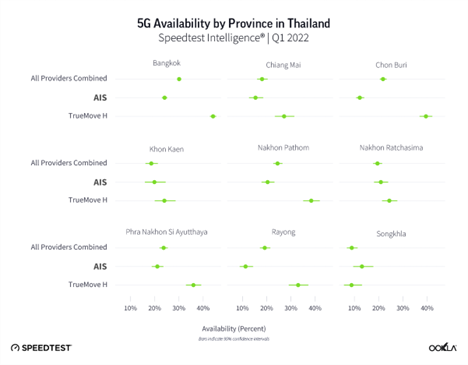
The ranking shifts when we compare 5G Availability – the percentage of users on 5G-capable devices that spend a majority of time with access to 5G networks. TrueMove H came first for 5G Availability at 37.9% during Q1 2022, a three percentage point improvement over Q4 2021. This was well above the rest of the Thai operators: AIS (18.7%), and dtac (7.9%). Based on our data AIS & TrueMove H had 5G Availability in all 77 provinces but TrueMove H 5G Availability was higher in most of the provinces as per Q1 2022.
This disparity we see between TrueMove H and AIS is largely down to the fact that AIS requires users to subscribe to a 5G tariff, as opposed to TrueMove H which allows greater access to 5G-enabled devices on its network. TrueMove H’s 5G Availability remains the highest via a combination of coverage and 5G handsets. The operator’s initial focus was to roll out 5G to most densely populated areas such as the Bangkok metropolitan area, in which over 90% of population is covered by 5G, followed by key locations. At the time of 5G network launch, TrueMove H offered 30 models of 5G smartphone under promotional prices, True 5G VR4K vision and True5G VR Headset, IoT equipment as well as gadgets. AIS rolled out a 5G network out to all 77 provinces, covering 78% of the population in Q1 2022, with a year end target of 85% population coverage.
At the same time, Thai operators continue to grow the number of 5G users, expanding the addressable market beyond early adopters; for example TrueMove H saw its 5G user base increase to 2.6 million in Q1 2022, AIS had 2.8 million 5G package subscribers and 3 million 5G handset on AIS network in Q1 2022.
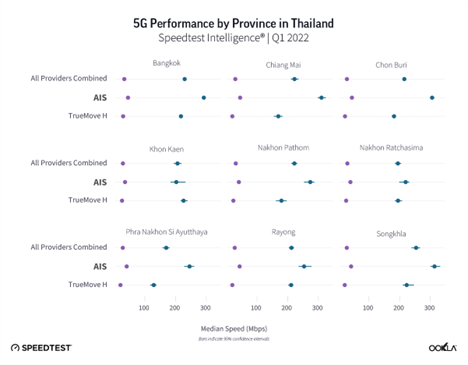
Songkhla tops the charts for median 5G download speed
Every operator takes a unique approach to regional strategy, so we looked closely at 5G performance in select regions during Q1 2022. Songkhla came top when it comes to median 5G download speed (253.44 Mbps), but ranked last in 5G Availability (8.9%), which points to low network congestion due to a lower number of users.
We removed dtac from the operator level comparison due to the low sample size. AIS came top in almost all regions, apart from Khon Kaen. AIS’s fastest median 5G download speed (313.35 Mbps) was in Songkhla.
Bangkok has the highest 5G Availability
In Q1 2022, Bangkok had the highest 5G Availability (30.1%), Songkhla ranked last in 5G Availability (8.9%). Ookla 5G Map® shows 215 commercial 5G deployments in the Bangkok area. What’s more, because Bangkok is more affluent than the rest of the country, smartphone adoption, including 5G, is higher than in the rest of the country. Due to the pandemic, Thai operators have actually accelerated their 5G rollout, starting with hospitals in Bangkok. At the end of 2021, AIS reported that its 5G network covered more than 99% of the population in Bangkok compared to 76% across the whole country. At the end of Q1 2022, dtac’s 5G network covered 34 provinces, though we have excluded dtac from the above ranking due to low sample count. Dtac has been focusing on network expansion using the 700 MHz band, resulting in capacity and coverage uplift, yet it is still lagging behind competition in uptake. Dtac reported that it will prioritize 5G expansion by expanding coverage to all of Thailand’s 77 provinces within the Q3 2022.
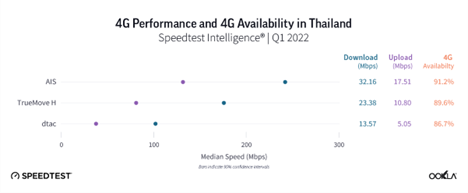
4G Availability close enough, AIS in the lead for 4G speeds
The leaderboard for 4G LTE performance in Thailand looked very similar to the 5G one during Q1 2022. AIS was in the lead (31.16 Mbps for download/17.51 Mbps upload), followed by TrueMove H (23.38 Mbps for download/10.80 Mbps for upload), and dtac (13.57 Mbps for download/ 5.05 Mbps upload), there was a major difference, however, when 4G performance is considered separately to that on 5G. AIS’s median download speed on all technologies combined was almost eight times higher than dtac’s, but AIS’s median download speed on 4G was just double of dtac’s. Furthermore, there was no substantial difference in terms of 4G Availability – the percentage of users on all devices who spend the majority of their time connected to 4G technology both roaming and on-network – across Thai mobile networks.
Consolidation wave across Asia-Pacific could stifle competition
Merger and acquisitions activity is heating up across the Asia-Pacific region with deals on the table across a number of countries including Thailand, Malaysia, Taiwan, and Indonesia. Thus far, only the merger between Indosat and Tri in Indonesia has received regulatory approval and been completed. This is true in Europe as well, ws we discussed in our recent article, with recent examples including the agreed joint venture between MasMovil and Orange in Spain and Iliad’s recent bid for Vodafone Italy.
A number of studies have attempted to assess the impact of mergers. For instance, in 2017 GSMA analyzed the impact of the 2012 Hutchison/Orange merger in Austria (a 4-to-3 merger) on quality using difference-in-differences (DD) and synthetic control methods. The study concluded that the merger in Austria had a positive and statistically significant effect on quality outcomes. The U.K. telecom regulator, Ofcom, in its Economic Discussion Paper on Market structure, investment and quality in the mobile industry analyzed a number of M&A activities. It concluded that the results of merger-specific analysis are mixed, as there is no evidence that mergers have generated improvements in network quality to the benefit of consumers. Instead, there is some evidence that both investment and average download speeds declined following some of these mergers. Closer to Thailand, Indosat Ooredoo and Hutchison 3 Indonesia (Tri) merged into Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison (IOH) to create a number two player in Indonesia with 26.3% market share as of Q1 2022. It was conditioned upon a number of factors, though, around improved geographic reach and network performance.
However, there are rare examples of a market moving towards duopoly. In 2011, Philippines mobile market became a duopoly after PLDT acquired Digitel. The deal was studied by regulators for seven months, the main issue being the large amount of the country’s 3G spectrum that the merged operator would control. It eventually passed on condition that PLDT gave up the 10 MHz 3G license held by one of its subsidiaries. Almost a decade later, a third player entered the Philippines, which we will discuss in an upcoming article.
The shape of the Thai mobile market
If approved, M&A would bring more MVNOs to the market
With close to 100 million mobile connections, Thailand’s SIM penetration of the population is 140%, meaning that on average a mobile subscriber has 1.58 SIMs. The market is served by four operators: AIS, DTAC, TrueMove H and the government owned National Telecom (NT). NT was formed in January 2021 via a merger of Communications Authority of Thailand (CAT) Telecom and TOT (Telephone Organization of Thailand).
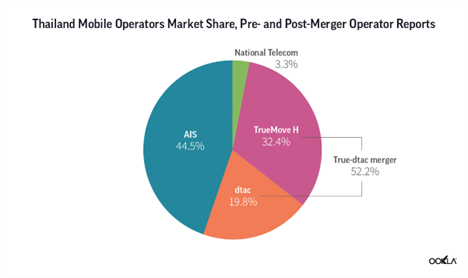
AIS, whose backers include Singtel Group, led the market with 44.5% of all mobile subscriptions, equivalent to 44.6 million subscribers, at the end of March 2022. By contrast, TrueMove H held 33.4% of the market share (32.5 million subscribers), with dtac claiming a 19.8% market share with 19.9 million subscribers. According to industry estimates, NT had less than 3.5 million subscribers in Q1 2022, equating to 3.3% market share. Currently, MVNOs hold a miniscule market share of the Thai market, under 1% combined. NT is the sole operator hosting MVNOs in Thailand since MVNOs were introduced in 2009, despite the fact that all of operators licenses’ terms and conditions have a clause that a minimum 10% of their spectrum capacity should be allocated to MVNOs. Opening up the market to MVNOs is often one of the conditions for M&A to go ahead.
The topic of mergers is widely discussed in Thailand; there have been a number of concerns raised. Thai consumer advocates and academics voice their disapproval of the M&A, saying consumers will be at a disadvantage due to less competition in the market. For instance, the People’s Network Protecting Public Interest claimed that the market would become a de facto duopoly with foreseen price increases of 20-30% in the long term. NT Telecom, which is both a competitor and a minority stakeholder in dtac, disapproved of the True-dtac merger.
The discussion as to who should approve the merger was put to rest when a legal subcommittee of the National Broadcasting and Telecommunications Commission (NBTC) concluded the telecom regulator has the power to approve or prohibit the planned merger. NBTC is still conducting studies on the impact of the merger, both short-term and long-term, as well setting up a number of independent committees to advise on the best course of action. Most recently, a panel that was tasked with determining whether the merger would have economic impact, M&A could reduce Thailand’s GDP growth by between 0.05% and 1.99%, and increase mobile prices by 2.03%-19.5% depending on the degree of collusion. Against this backdrop, it is hard to imagine that the merger would get a green light.
If the merger goes ahead, the newly combined entity will become the number one player in Thailand with a 52.2% market share, ahead of the current market leader, AIS. However, it takes time for the companies to merge their operations and it is most likely that in the short term both companies will use their separate brands while working out the go to market proposition. Also the companies’ execs at a recent seminar were at pains to assure that there will be no price hikes if the merger goes ahead, instead because of the economies of scale there will be more investment into the market resulting in more innovation and better customer experience.
If approved, M&A would change the spectrum landscape
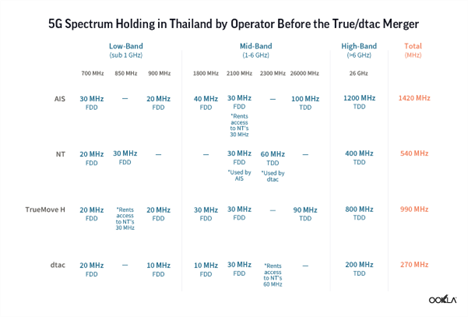
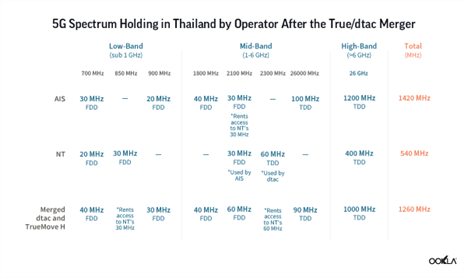
As it stands right now, AIS has the largest amount of 5G spectrum — a total of 1,330 MHz — across low-, mid-, and high-frequency bands. In May 2022, AIS added a further 10 MHz of bandwidth on the 700 MHz spectrum from NT due to the deal with NT Telecom. With this deal, AIS will increase its bandwidth to 40 MHz from August 2022 onward, which should improve its 5G coverage.
AIS and TrueMove H deployed their initial 5G networks on the 2600 MHz spectrum, while dtac used frequencies in the 26 GHz band. All operators, except for NT, also deployed 5G in the 700 MHz spectrum band when it became available for use in early 2021, following the completion of broadcasting service migration. NT is yet to deploy 5G.
Thanks to the merger, dtac would have access to True’s mid-band spectrum, which should substantially improve its performance. Furthermore, there is another C-band spectrum auction planned in 2022 (3.4-3.7 GHz band). This should have a positive effect on the 5G download speeds as we have seen in the USA when since deployment in the C-band, Verizon’s 5G speeds have set it apart from AT&T.
However, it is common practice that operators that undergo mergers have to divest part of their spectrum as an M&A condition. For example, this was the case when Hutchison 3G acquired Orange in Austria, Hutchison 3G bought Telefonica in Ireland and Telefonica merged with E-Plus in Germany.
The benefits of scale are obvious
Fixed Mobile Convergence (FMC) bundling is offered by most operators in Thailand due to competitive pressures coming from TrueMove H and AIS. The merger could enable convergent offerings from dtac too, which is solely a mobile player, and would allow it to offer better service in terms of coverage and further expand its market share. According to Analysys Mason, FMC penetration will continue to increase in Thailand, and if the merger is blocked, dtac’s competitive standing will be further disadvantaged.
On the other hand, True Corporation has a portfolio of services:
- TrueMove H — mobile operator, which also offers NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT).
- TrueOnline — broadband internet and fixed-line. It is the largest fixed broadband provider with a 46.7% market share.
- TrueVision — Pay TV, digital TV and content provider and an online game and influencer network; 3.5M subscribers.
- True Digital Group — Digital media, data analytics, cybersecurity, IoT, integrated digital health, digital solutions and True Digital Academy.
The merged operator NewCo would remain at its core a telecommunication player but would extend its reach to support the digital transformation of Thailand, in line with Thailand 4.0 vision. The quoted benefits of the “amalgamation” include:
- Improved 5G coverage with better network quality, reliability and speed.
- More value-driven convergence or products and services thanks to access to a wider ecosystem of partners.
- Utilization of consolidated infrastructure such as outlets to expand its outreach to deliver on Thailand 4.0 policy.
- Greater opex and capex cost efficiencies when deploying 5G networks thanks to the benefit of scale. As a result improving the quality of telecom infrastructure and customer satisfaction.
- Streamlined efficiencies will deliver better consumer experience and will enable NewCo to invest in future technologies and networks.
- Positioning Thailand as a regional technology hub.
The NewCo will operate:
- Telecom services and the sale and distribution of mobile devices via subsidiaries dtac, TriNet, and TrueMove H — using the 700 MHz, 850 MHz (under agreement with NT), 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, 2100 MHz, and 2300 MHz (under agreement with NT) spectrum.
- Broadband internet provider via TrueOnline.
- Pay TV, digital TV, and content provider via TrueVisions.
- Portfolio of digital services via True Digital Group, and new businesses through artificial intelligence, cloud technology, smart devices, smart cities, amongst others.
- Venture capital investments, with the intention to raise VC funding of USD 100-200 million with partners to invest in promising digital startups.
The merged operator could provide more competition to AIS across all market segments, not only mobile. AIS Fiber, for instance, holds a 14% market share and differentiated its services with value added and bundling packages. NewCo would build on existing TrueOnline offering and could take a convergent offering to a new level, e.g. quadplay.
While we await the final decision on the merger, it is clear that dtac is falling behind its competitors when it comes to 5G performance. The recently announced National 5G Alliance aims to further promote the role of 5G in enabling digital transformation. We will monitor Thai operators’ performance and wait for the results for the upcoming mid-band spectrum auction to see whether this will close the performance gap. In the meantime, you can compare mobile performance across operators and countries using Speedtest Intelligence.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.