Key takeaways
- The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the need for digital transformation, part of the EU-level funding will be available to drive digital transformation.
- Spectrum auctions have been delayed across the region. While Slovenia and Croatia have already completed spectrum auctions across all of the 5G pioneer bands, Poland lacks clear timelines and risks being left behind.
- Bulgaria leads in 5G median download speeds and 5G Availability. Its capital, Sofia, takes the top spot across the capital cities when it comes to median 5G speed and 5G Availability.
- Poland doesn’t fare well compared to other CEE countries. Poland came last in the median 5G download speeds ranking and its 5G speeds were just over double that of 4G. More importantly, though, it also seems that Polish end users don’t see the additional benefits 5G can bring, which depresses demand.
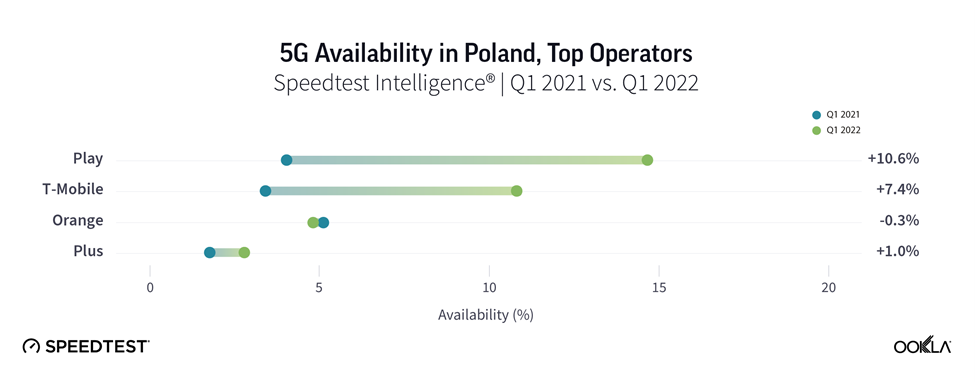
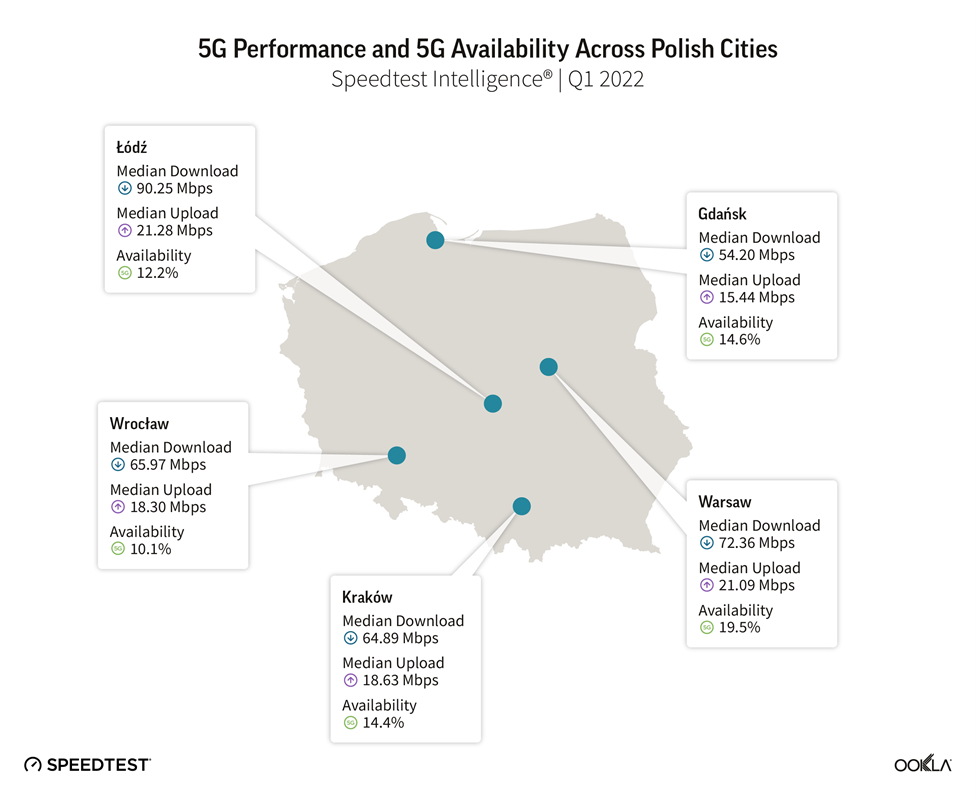
- Plus has the fastest median 5G speeds while Play wins 5G Availability. Łódź has the fastest 5G network among major Polish cities.
The EU funds set to stimulate digital transformation
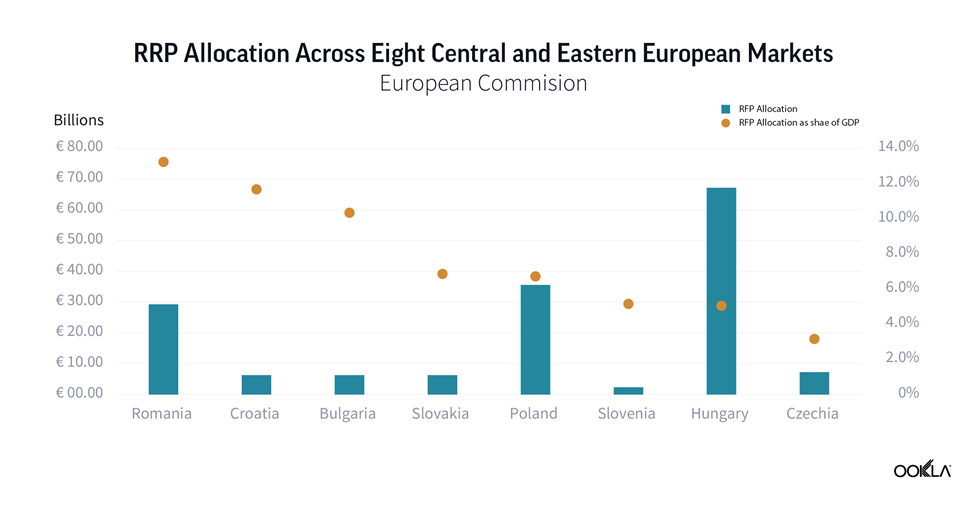
An unprecedented amount of funding available to European Union member states has been approved to mitigate the economic and social impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. The NextGenerationEU recovery fund totals €750 billion. The vast majority, €672.5 billion, is allocated to the Recovery and Resilience Plans (RRP), distributed between loans (€360 billion) and grants (€312.5 billion). All funds must be spent by 2026.
While not all these funds will drive investment into telecoms, some will have indirect impact such as green technology — see our thoughts on the discussions around Net Zero at MWC 2022. There are six pillars, one of which is digital transformation, which has over 20% of the national RRPs funding allocated. Digital transition projects include investment in R&D, deployment of new digital technologies including expansion of ultrafast broadband and 5G connectivity, and the digital transformation of the economy. The money is there for the taking, it is up to the countries to take advantage of it and funnel it into technology such as 5G to underpin economic growth.
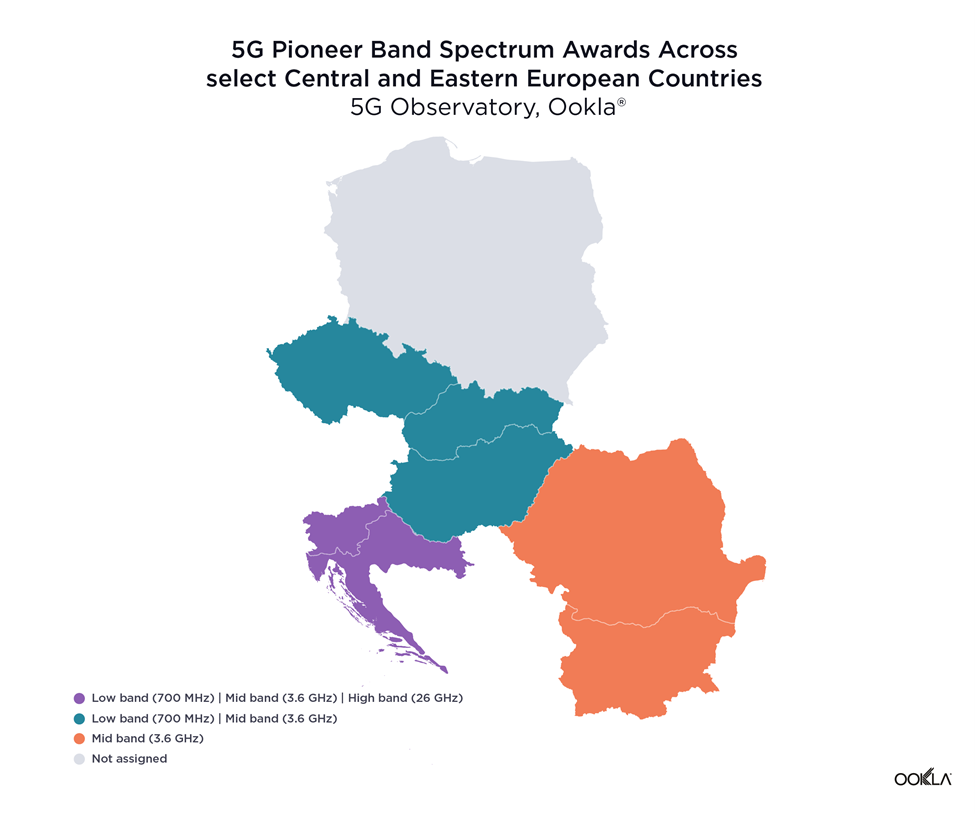
Mid-band is most assigned spectrum across Central and Eastern Europe
We have reflected on the progress across Europe in this article. Now, we turn our attention to Central Eastern European (CEE) countries. According to GSMA Intelligence data, the vast majority of operators across the eight CEE countries — 24 out of 31 — have already launched 5G services.
As per the EC 2016 5G Action Plan, countries across the EU were meant to make low-band spectrum available for use by June 30, 2020, and mid- and high-band spectrums by December 31, 2020. At the EU level, there are three 5G pioneer bands as follows:
- Low-band: 700 MHz (703 – 733 MHz and 758 – 788 MHz)
- Mid-band: 3.6 GHz (3,400 – 3,800 MHz)
- High-band: 26 GHz (at least 1000 MHz within 24,250 – 27,500 MHz)
The delays related to spectrum assignment range from the impact of COVID-19 on schedules to cross-border coordination with non-EU countries to weak demand from the operators’ side. However, most countries included in this analysis have already assigned at least one band for 5G, with a notable exception of Poland.
Poland is yet to carry out a 5G spectrum auction — the planned sale of a C-band spectrum in Poland was postponed multiple times for various reasons. In March 2020, Poland announced the 3.6 GHz spectrum auction to be awarded by June 30, 2020. However, due to the pandemic, Polish authorities suspended all administrative proceedings, and the current holdup is due to legislative issues.
Furthermore, Poland is also exploring a controversial law to establish a state-owned 5G network, which would be operated by a state run operator — Exatel — in the 700 MHz band. The 700 MHz band is problematic because it requires coordination across the eastern borders (Belarus, Russia and Ukraine), which will delay spectrum assignment.
Slovenia and Croatia have forged ahead and become the only two countries that have already completed spectrum auctions across all of the 5G pioneer bands. In April 2021, Slovenia’s Agency for Communications Networks and Services (Akos) concluded the sale of frequencies in the 700 MHz, 1500 MHz, 2100 MHz, 2300 MHz, 3500 MHz and 26 GHz bands. In August 2021, the Croatian Regulatory Agency (Hakom) auctioned frequencies in the 700 MHz, 3600 MHz and 26 GHz bands. Furthermore, Miran Gosta, director of Hakom, recently announced that a new auction is being prepared for the frequencies that are already in use and will expire in 2024 such as 800 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, 2100 MHz and 2600 MHz bands.
Bulgaria leads 5G speeds
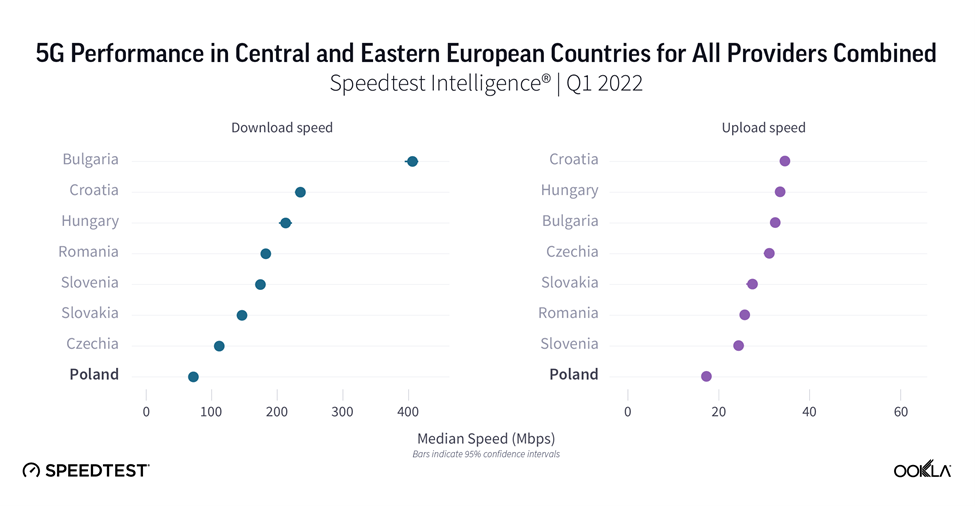
The important question is whether delays in spectrum assignments and supporting multiple network generations have affected the operators’ ability to deliver on 5G’s promise of faster speeds. According to Speedtest Intelligence®, the 5G median download speeds across the eight countries range from 73-407 Mbps. Bulgaria is the fastest at 406.97 Mbps, followed by Croatia, Hungary, Romania, Slovenia, and Slovakia. Czechia and Poland are trailing behind, at 112.53 Mbps and 73.12 Mbps, respectively.
Bulgarian operators took an active role in spearheading 5G development. In September 2020, Vivacom launched the first commercial 5G network via Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) in 1,800 MHz and 2,100 MHz, followed by A1 in Sofia using 3,600 MHz, and Telenor in early June 2021 in the biggest cities in Bulgaria in the 3,600 MHz band.
In April 2021, Vivacom Bulgaria won 100 MHz in the 3.7-3.8 GHz band for BGN4.6 million (€2.35 million) but it had already launched the 5G network before with a temporary license in November 2020. András Pali, Vivacom CTO stated in an interview that the operator plans to invest €120 million in infrastructure in 2021. Vivacom utilizes DSS, combining frequencies in 1.8, 2.1 and 3.6 GHz bands for 5G, so there is no compromise between coverage and speed. A1 Bulgaria, on the other hand, uses a dedicated 100 MHz band. Between the commercial launch in April and October 2021, A1 Bulgaria has seen the number of active users rise by 448% and the traffic generated by them by 771%, in excess of 90 terabytes (TB) in October 2021.
Furthermore, Bulgaria’s recovery and resilience plan assigned 26% of the €6.3 billion budget to digital transition. The plan includes measures to stimulate digital transformation, including significant investments and reforms in digital connectivity to increase the coverage of very high capacity networks in rural and sparsely populated areas and to create a favorable environment for the deployment of 5G networks and digital infrastructure.
A few operators have rolled out 5G networks before having access to a dedicated 5G spectrum holding, instead using their existing spectrum holdings via DSS or temporarily allocated spectrum. Looking at the data for Poland, there is a link between lack of dedicated spectrum and median download speed. 5G speeds in Poland are just double the speeds of 4G, compared to Romania, Slovakia, Hungary, and Slovenia where 5G speeds are over five times faster than 4G. Since operators in Poland deployed 5G utilizing their existing spectral assets — in 2.6 GHz and 2.1 GHz — they are not able to take advantage of the benefits that mid-band spectrum brings to 5G deployments. We have reflected on how mid-band spectrum boosted 5G speeds and coverage in the U.S.
5G Availability skyrocketed in Bulgaria during 2021
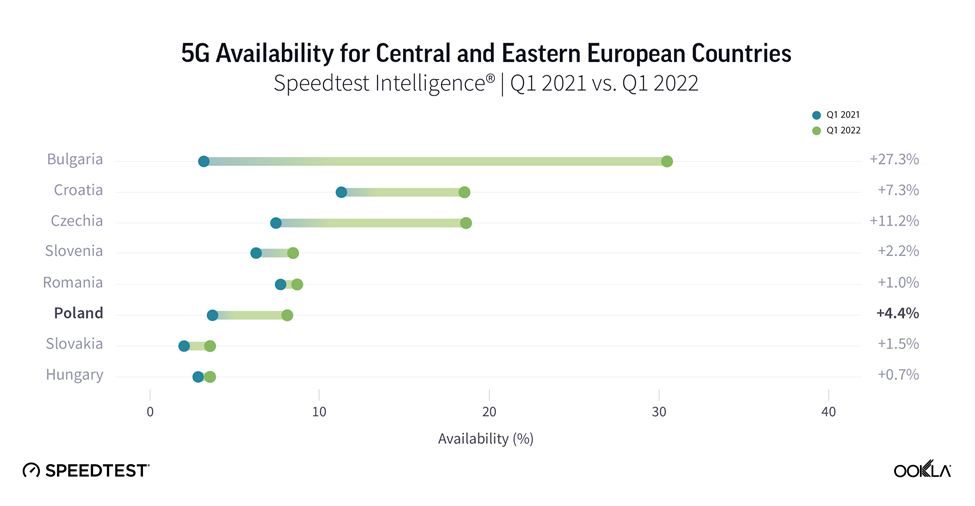
Speedtest Intelligence data put Bulgaria first in terms of 5G Availability (the proportion of users of 5G-capable devices who spend a majority of their time on 5G networks) within its regional peers. During 2021, 5G Availability in Bulgaria increased ten-fold, from 3.0% in Q1 2021 to 30.5% as of Q1 2022. This is partially thanks to operators broadening their portfolio of 5G capable devices, e.g. in June 2021, 55% of Telenor’s (now Yettel) smartphones on offer were 5G capable and offering 5G tariffs at no additional cost.
Croatia performed relatively well when it comes to 5G Availability, which increased from 11% in Q1 2021 to 18.5% in Q1 2022.The Croatian operators’ 5G license comes with coverage obligations amounting to 90% of urban areas, 99% of highways and 95% of railways by 2025. Furthermore, the license obligations include 25% rural areas coverage by 2025 and 50% by 2027. According to Hakom, 5G coverage and availability is at 60-70%.
However, five countries still had 5G Availability below 10% in Q1 2022, down from seven in Q1 2021. In Hungary, there is a public initiative in support of 5G uptake in a tune of HUF 5 billion (€13.15 million) to help consumers migrate away from 3G devices to 4G/5G smartphones in face of the upcoming 3G network sunset. On May 9, 2022 the Hungarian telecom regulator — NMHH — began a second phase of its mobile phone subsidy: owners of 2G or 3G devices can claim HUF 20,000 (€52.26) towards a purchase of a new 4G or 5G smartphone.
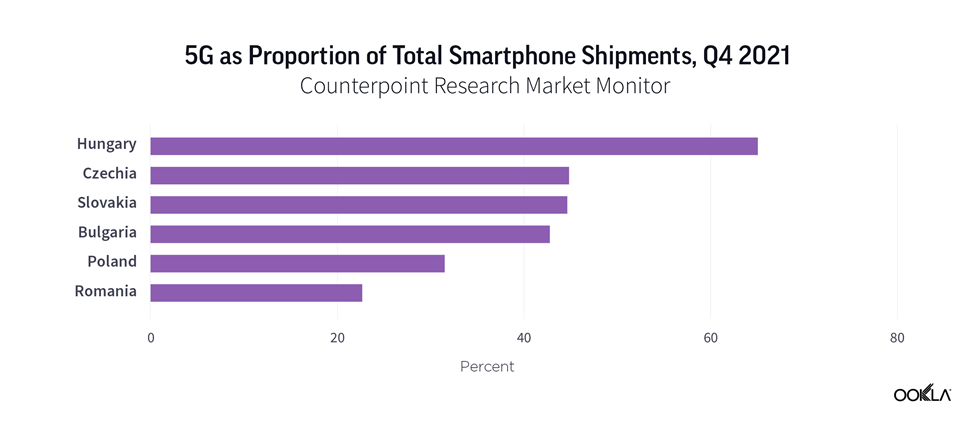
It isn’t surprising to see that Hungary came first when it comes to 5G smartphone shipments across a number of CEE countries. According to Counterpoint Research, 5G smartphones accounted for 65.1% of total smartphone shipments in Hungary in Q4 2021. In Czechia, Slovakia and Bulgaria, 5G smartphones account for two in five smartphones shipped. In Poland, this is almost one in three. Romania comes last. Although, these figures do not directly translate into direct sales to customers as shipments refer to selling into retail channels and point to an increased appetite for 5G devices. A key driving factor behind this is a growing availability of lower price tiers 5G smartphones. For instance, realme is seeing success with affordable 5G smartphones in Europe.
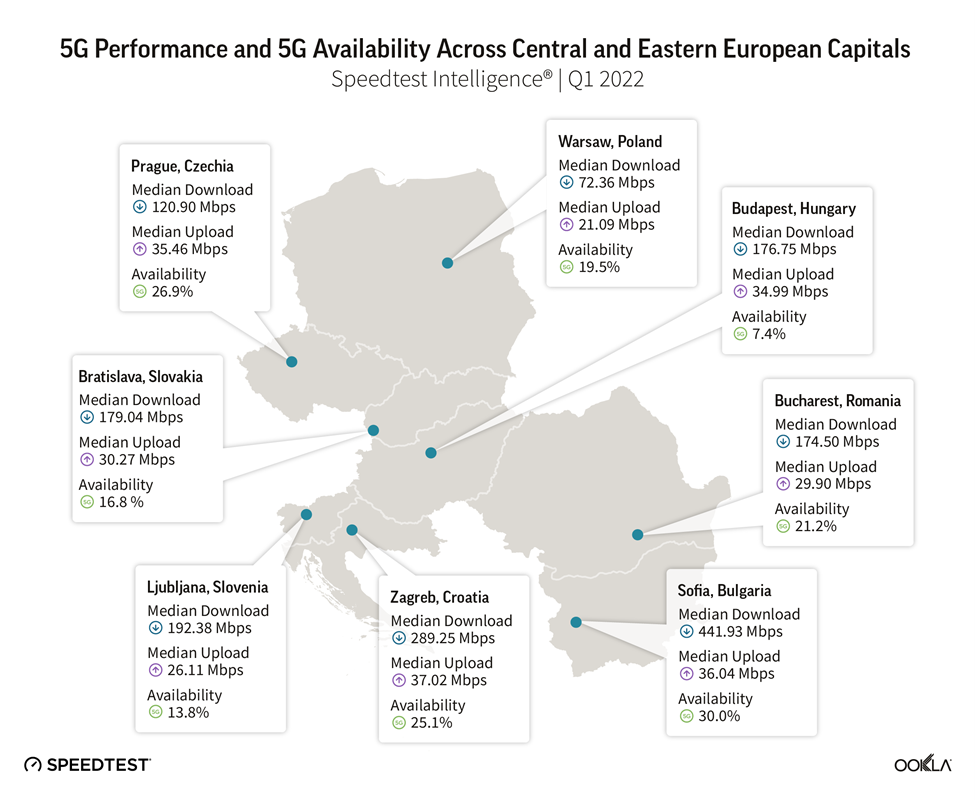
Sofia comes first in 5G median download speed and 5G Availability
Given that Bulgaria had the fastest 5G and the best 5G Availability among its peers, it isn’t surprising its capital came first as well in the ranking of regional capitals, at 441.93 Mbps median download speed and 30% 5G Availability in Q1 2022. A1 Bulgaria started a test run already at the end of November 2020 in Sofia and Burgas, and they became the first 5G city in the country with an outdoor population coverage of over 90%.
Prague performed well when it comes to 5G Availability. In April 2022, the Prague metro area was fully covered by 5G networks thanks to a cooperation between Czech operators: T-Mobile, Vodafone, O2 and CETIN, and the Prague municipality. All of the Czech operators sunset 3G networks in 2021 to refarm the frequencies for 4G and 5G. The largest operator by number of connections, T-Mobile Czechia had more than 600 5G base stations covering 10.4% of the population in September 2021, and it planned to increase coverage to 25% by the end of the year. T-Mobile uses Ericsson and Huawei for its 5G network, which utilizes the 1800 MHz, 2100 MHz, and 700 MHz bands. The smallest operator, Vodafone Czechia, covered 70% of the population with a 5G network reaching 7 million Czechs in May 2022. Vodafone is committed to extending its network reach, at the moment it uses 3.5 GHz for 5G, but shortly it will start using the 700 MHz band as well as the refarmed 3G spectrum.
Poles need more education on the benefits of 5G
When it comes to 5G performance, Poland doesn’t fare well compared to other CEE countries. Poland came last in the median 5G download speeds ranking and its 5G speeds were just over double that of 4G. It is the only country that has not yet awarded 5G spectrum. More importantly, though, it also seems that Polish end users don’t see the additional benefits 5G can bring, which depresses demand.
According to the UKE’s enterprise survey, 78.2% of enterprises in Poland have heard of 5G. Good. However, the majority of enterprises claim that the current mobile parameters are enough to carry out their business activities across three measures: speed (88.6%), reliability (86.7%), and performance (85.9%). Given that the current 5G networks in Poland do not deliver on gigabit speed promises, this isn’t surprising.
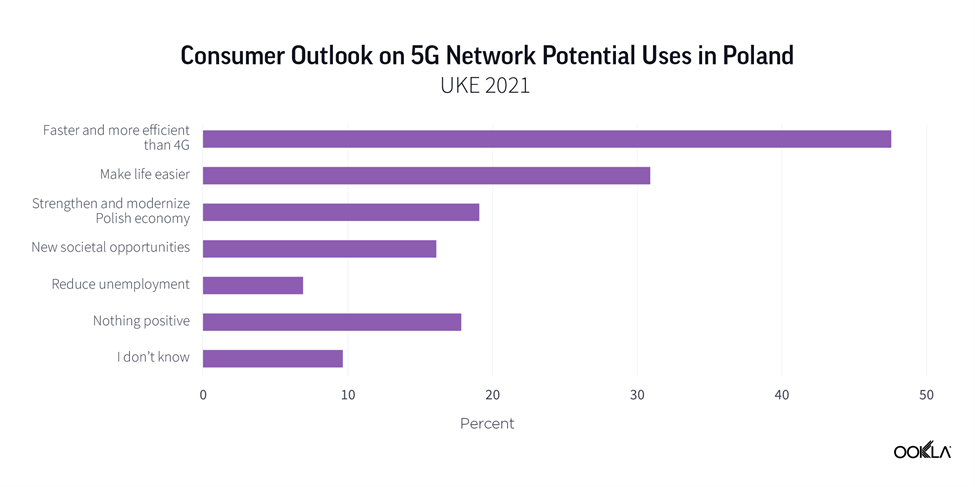
From a Polish consumer point of view, 73.8% are familiar with the term 5G. This comes with a downside, though, just over half of respondents (57.4%) believe that 5G poses health risks.
Asked what are the key benefits of 5G networks, almost half of respondents (47.5%) state that 5G will be faster and more efficient than 4G. Less than a third (31%) see 5G networks making people’s lives easier. The third preferred option is 5G’s ability to strengthen and modernize the Polish economy. Still, 18% do not see any positive outlook for using a 5G network. This can partially explain why 5G Availability in Poland is sub-10%.
5G is not only about speeds. 5G is seen as an avenue to bring additional value to the economy and society. According to a study from Ericsson Poland, the Polish economy could gain over €17 billion from 5G implementation by 2040. Considering the lack of a clear timeline for the 5G auction, the risk that Poland will fall further behind its peers is real.
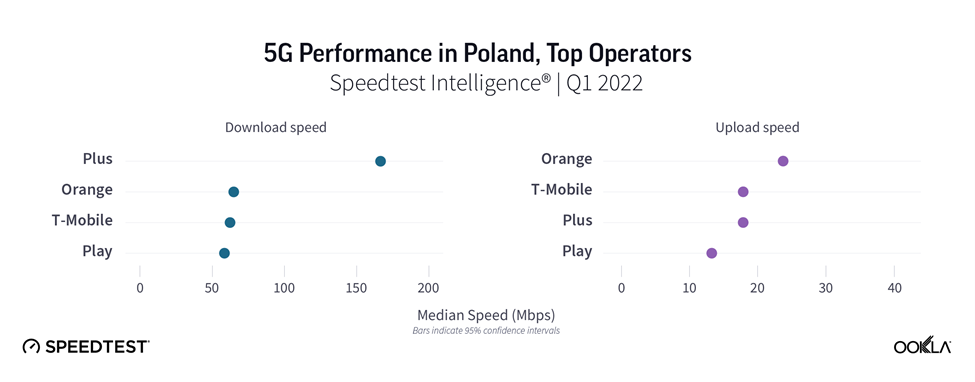
Plus led on 5G download speed in Poland
We compared 5G performance across Polish operators using Speedtest Intelligence. Plus was a clear winner, reaching median download speeds of 167.37 Mbps speeds in Q1 2022, ahead of Orange, T-Mobile, and Play. There isn’t a substantial difference in median upload speeds across the operators.
All of the Polish MNOs rolled out 5G networks tapping into their existing spectrum in a Non Standalone (NSA) mode, which relies on the underlying 4G/LTE technology. The 5G auction is now dependent on ongoing consultations about the National Cybersecurity Law Project, to be discussed by the Polish Parliament. The Law may impact network equipment decisions amongst the players, e.g. Play is using Huawei and Ericsson for base stations.
Polkomtel, trading under the Plus brand, launched the country’s first commercial 5G network in the 2.6 GHz band, utilizing 50 MHz of spectrum in May 2020. Apart from Plus, all other operators deployed 5G using DSS in the 2.1 GHz spectrum band, which can partially explain why they have lower speeds.
Orange Poland, like other countries within Orange Group, will roll out 5G Standalone (5G SA) in partnership with Ericsson. This will enable 5G network slicing and private networks development. In anticipation of the 5G auction, and to stimulate new 5G use cases, the operator launched Orange 5G Lab testing services such as AR, AI utilizing the spectrum allocated by the UKE for testing 5G in the 3.6 GHz band.
Play had the best 5G Availability in Poland
According to Counterpoint Research, smartphone shipments in Poland have almost tripled during 2021, driven by the challenger brands such as realme, OPPO and Xiaomi (including Redmi and POCO). Polish operators also continue to promote the sale of 5G-capable devices. 5G smartphones as a proportion of smartphone sales ranged between 36% for Orange, 40% for T-Mobile, and 45% for Play. Yet, Play has sprinted ahead the pack when it comes to 5G Availability, and T-Mobile is catching up leaving Orange and Plus behind.
This is surprising because the Play’s 5G network doesn’t necessarily have the widest reach. As of year-end 2021, Plus’ 5G network extended to 19 million people, followed by Play with over 13 million, T-Mobile (11 million) and Orange (6.3 million). Translating this into population coverage using 2021 census data (38.18 million people), this equates to 50%, 34%, 29%, and 17% population coverage.
Play, part of the Iliad Group, had the best 5G Availability, likely because of aggressive marketing and discounts combined with a large portfolio of 5G devices and the cheapest tariffs. Recently, Play had secured a PLN 500 million (€107 million) credit facility under the Operational Programme Digital Poland (POPC) from BGK, which will also use to roll out 5G services.
The mobile operators continue to invest in 5G network rollouts. For instance, T-Mobile extended its partnership with Nokia to include the modernization of RAN as well as rollout of 5G services. The operator plans to use 4G and 5G DSS on the lower band and. when available, the 3.5 GHz band for dense urban areas. T-Mobile targets to finish 2022 with 3,500 5G base stations and 30% population coverage. T-Mobile shut down its 3G network in the 2,100 MHz frequency band in October 2021. It has also embarked on the 3G network shutdown, aiming to realize the 900 MHz used for 3G and refarm it to LTE and 5G in 2023.
The spanner in the works to achieve wide 5G availability is the controversy around 5G auctions. In October 2019, the four leading mobile operators (Plus, Orange, Play and T-Mobile), the state-owned telecom operator Exatel and the Polish Development Fund (PFR) signed a memorandum of understanding to build a nationwide infrastructure. This will be owned by the state via a special-purpose entity called Polskie 5G. The Polish regulator has proposed to assign the entire 700 MHz band (2×30 MHz) to this new entity, with a view to first provide connectivity for public protection and disaster relief services, while making it available to all operators. Reserving spectrum for vertical use is not new, we have discussed this in our recent article; the novelty here is the band and amount. The 700 MHz band is key for providing wide coverage and in-building penetration. In our recent webinar, Eric Brands from KPN explained that KPN scores well in 5G Availability, partially because they have access to low band 5G spectrum (700 MHz).
Łódź has the fastest 5G network among major Polish cities
Łódź came top as the fastest city in Poland with 90.25 Mbps in Q1 2022, it is also a hotspot for operators’ innovation. Orange deployed a 5G campus network in the Lodz Special Economic Area where 40 start-ups working in the accelerator will be able to use the infrastructure. Ericsson has provided the infrastructure for the economic area: ten antennas working on the 3.6 GHz and 2,100 MHz bands, covering approx.1,000 square meters.
T-Mobile is testing 5G SA in Łódź to enable new services for both consumer and B2B customers, including VoNR (Voice over New Radio) services on the 5G network. The 5G SA network is utilizing the 2,600 MHz band.
The Polish capital, Warsaw, is just slightly ahead of the rest in terms of 5G Availability.
We’ll be watching 5G performance closely in Poland using Speedtest Intelligence. If you want to learn more about how Speedtest Intelligence can help you benchmark your 5G performance against competitors, please inquire here.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla