Around the world, artificial intelligence (AI) is automating functions and making new services possible with breakthroughs in low-cost computing power, cloud computing services, growth in big data and advancements in machine learning (ML) and related processes. AI has the potential to radically alter and improve the way governments, organisations and individuals provide services, access information and improve their planning and operations.
This study examines the current use of AI in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). The report maps a sample of 450 AI start-ups in LMICs in Africa and South and Southeast Asia, most of which are early-stage, home-grown solutions with a focus on the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It also explores trends and challenges in business models, barriers to innovation, and AI’s ethical and responsible use:
- Business intelligence and analytics emerged as a clear leader in the use of AI, as it captures a wide range of business services solutions, from accounting and decision making to customer service;
- Healthcare had the second-highest number of use cases and clearly benefits from AI solutions, from sophisticated diagnosis and treatment options and hospital management systems to lifestyle change recommendations and healthy eating habits; and
- Food and agriculture followed with a range of AI-based services, including services for identifying and remedying crop diseases, linking producers more effectively to buyers and markets and maximising crop yields based on climatic and soil conditions.
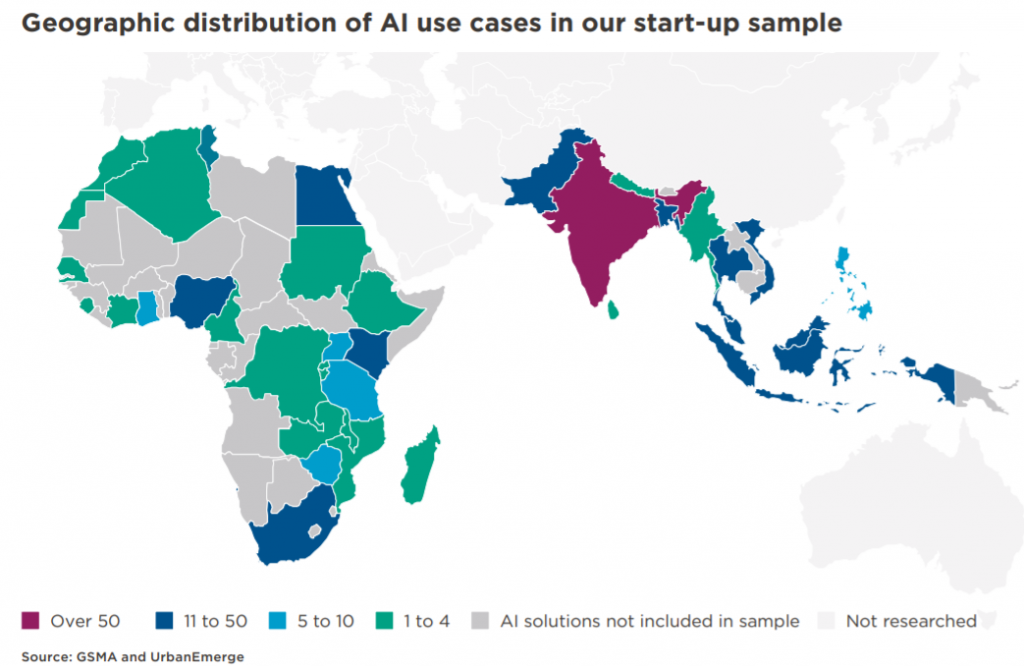
Focusing on use cases by SDG, the most significant contributions are to SDG 8 – decent work and economic growth, and SDG 9 – industry, innovation and infrastructure. There is also a strong focus on food and agriculture (SDG 1 and SDG 2), particularly relating to poverty reduction and climate-smart agriculture. Another dominant industry to align AI with SDG 3 is healthcare.
To grasp the business models, this study looks at three vital factors:
- Monetisation;
- Consumer segments; and
- Outlook.

The results of the use case mapping, along with existing industry analysis and interviews, show that the majority of AI companies globally remain AI-enabled, although there are a growing number of AI-first companies. AI-enabled companies use AI to enhance their offerings, while AI-first companies use AI as their core product. This distinction determines the core competency and unique value proposition of all AI companies.
The report concludes by highlighting that there are many fundamental questions about data protection, ingrained bias and the responsible use of AI. While AI has the potential to achieve social good, positive outcomes are not necessarily guaranteed. AI can improve efficiency and productivity, but it may also deepen inequalities lead to increased inequalities among and within countries, thus hindering the achievement of the SDGs. Since increased use of data introduces further privacy and ethical concerns, AI solutions should be guided by sound privacy and ethical principles.
The GSMA Mobile for Development (M4D) Central Insights Unit is an initiative supported by the UK Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO), the GSMA and its members.




