As the mobile money industry begins to give more serious attention to interoperability, MMU is working with industry players to advance the conversation and support early movers and on-going implementations.
As part of this work, MMU released a new paper titled ‘A2A Interoperability’ last week at Mobile World Congress in Barcelona that we co-authored with Consult Hyperion. This paper looks at account-to-account (A2A) interoperability in mobile money, which is defined as enabling direct transactions both between different mobile money schemes and between mobile money schemes and banks. This definition of interoperability was useful to reach a certain focus of the paper, although it also meant that we had to leave interesting use cases out for this paper.
In the hope of demystifying the topic of interoperability, the paper looks systematically at six different A2A interoperability implementation options, taking examples from the banking and payment sectors across the world.
As there are many ways to achieve A2A interoperability, it is important to identify the most appropriate solutions for a particular market. The paper introduces an evaluation framework that can help operators to ask the right questions around each interoperability implementation option available.
It quickly becomes clear that the market conditions – how mature the banking and payments sector is or what financial infrastructure is available – influence what an optimal solution for that particular market would look like. It is likely that we will see a few different models emerge depending on the composition of the markets where it is implemented.
Considerations
It is crucial that an interoperable solution maintains the attributes that have made mobile money so successful to date; that transactions are affordable, in real-time and that the services are accessible for all. The affordability and accessibility considerations are particularly important to allow mobile money to continue to reach populations currently without formal financial tools at hand. Further, a major reason we identified for under-utilization of interoperable banking systems was excessive costs to use the service.
In order to move ahead with a successful implementation, we believe that a collaborative approach is necessary. When working on this topic, it is important for the industry players to engage in a dialog with the regulator and policy makers to ensure that the work is in line with regulation and the policy objectives. An on-going dialog also ensures that regulators and industry players learn from each other as this most likely will be a new topic for both. In the appendix of the paper you will find draft terms of reference to start an industry task force for discussing and managing the implementation of the interoperability solution chosen.
Let us know your thoughts and feedback about the A2A Interoperability paper by email, [email protected], or in the comments box below. The next steps will be to continue to explore commercial models to make interoperability become a positive catalyst for transactions, and the team at GSMA are available for anyone interested.
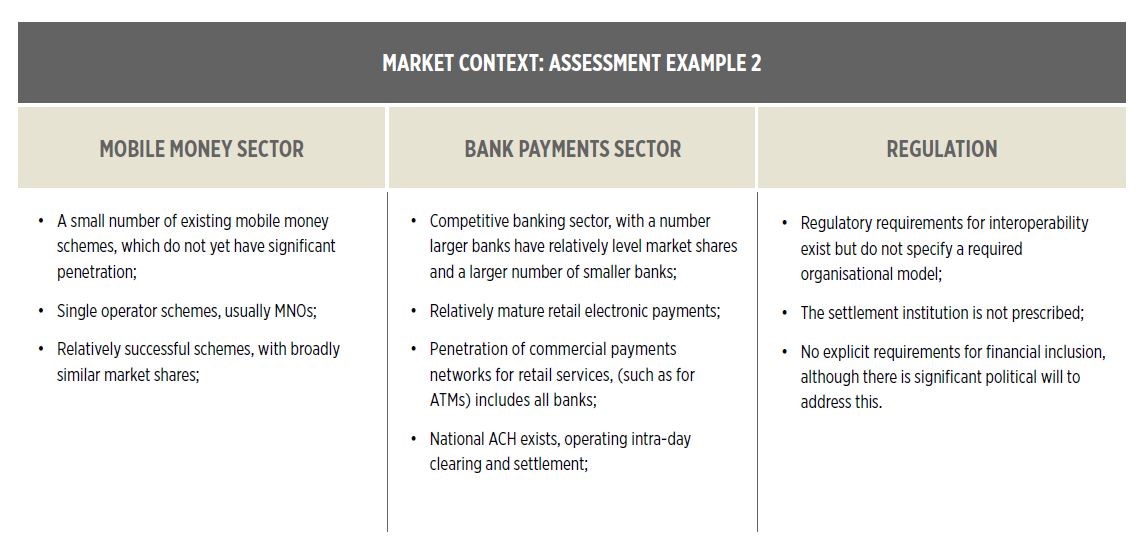
Below is an example market assessment using the evaluation framework introduced in the paper.
Market example context
Worked evaluation framework for the example market
Evaluation summary