5G Transformation Hub
How 5G is enabling Smart Hospitals
5G connectivity in operating theatres can boost the efficiency of medical training fivefold
In Hong Kong, CUHK Medical Centre (CUHKMC) is using HKT’s high throughput and low latency 5G to support innovative medical applications, such as remote consultation, remote training, tele-medicine, and potentially treatment guided by augmented reality (AR) services. HKT has built full 5G coverage across the entire CUHKMC hospital, which has 28 operating rooms, 49 consultation rooms and 516 beds for in-patients.
Select a project
Contents
Challenge
In cases where patients need specialist advice and help, front-line medics have historically referred them to an expert in the relevant field of medicine for both consultations and treatment, such as surgery. In-person consultations and operations with specialists can take time to arrange, delaying treatment, and can be expensive. Similarly, in-person training of medics can be both expensive and time-consuming.
Solution
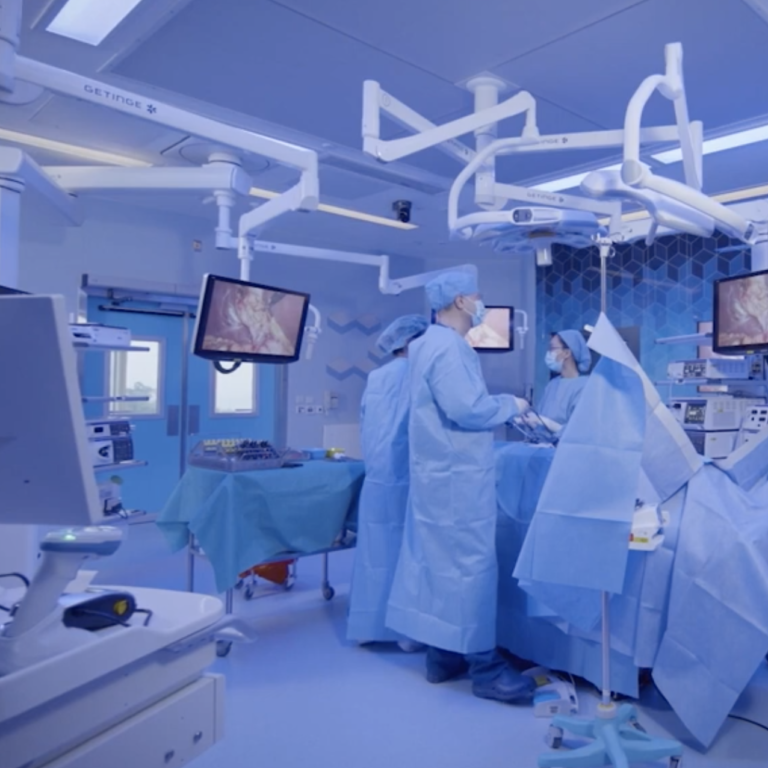
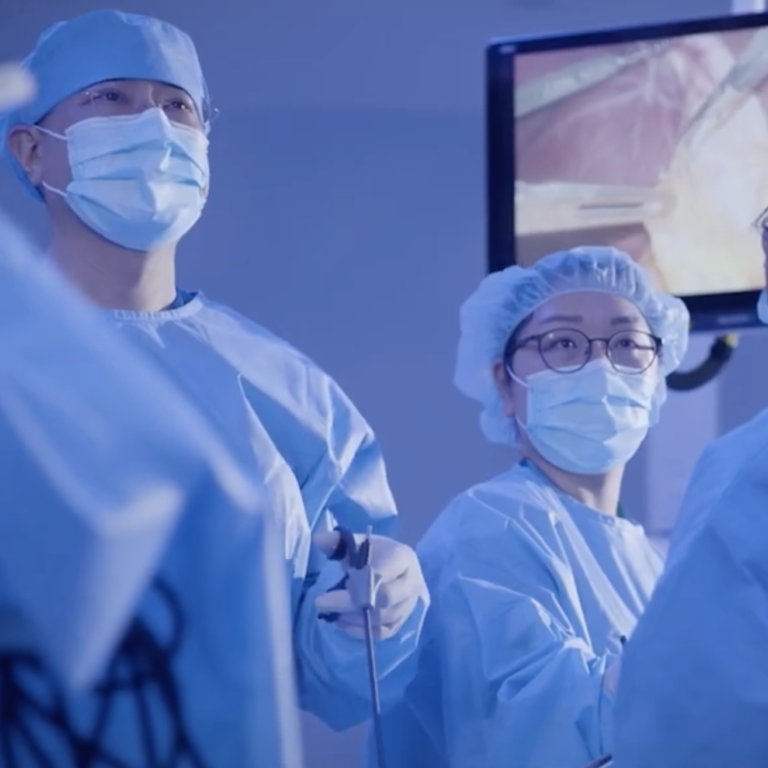
CUHKMC operating theatres are fully covered with 5G, which is used to transmit multiple 4K video streams of the surgery, as well as images captured by medical equipment, such as an endoscope. Viewed on a mobile device or PC, these visuals can help the remote specialist provide expert opinion on the surgery. Leveraging 5G connectivity, CUHKMC can also provide a virtual follow-up consultation for patients, reducing the need for them to revisit the hospital. At the same time, the 5G connectivity is being used to enable remote clinical training for medical students and to support international medical conferences.
Impact & Statistics
The 5G connectivity is enabling professors at CUHKMC to demonstrate live surgical procedures to more than 20 students simultaneously – that amounts to fivefold increase in efficiency compared with having a handful of students watch a procedure in-person inside the operating theatre. According to HKT, its 5G network is able to support speeds of over 1Gbps with latency of less than 10ms. Such connections are fast and responsive enough to support very high quality 4K video, 3D imaging, virtual reality (VR), AR and multi-camera views, thereby providing a fully immersive experience for remote clinicians and students.
Wider Implications
Reliable high-speed 5G connectivity could transform healthcare by enabling smart hospitals to improve the patient journey and overall operational efficiency. As 5G connectivity could support a wide array of smart hospital applications such as remote consultation (doctor-to-doctor), remote training (doctor-to-student) and telemedicine (doctor-to-patient), resources in the hospital can be optimised and patients can receive the best possible care.
Stakeholders
CUHK Medical Centre (CUHKMC) and HKT
02
How 5G is enabling Smart Hospitals
5G connectivity in operating theatres can boost the efficiency of medical training fivefold
Reliable high-speed 5G connectivity could transform healthcare by enabling smart hospitals to improve the patient journey and overall operational efficiency. For example, 5G can transfer 4K ultra high definition medical videos and images, such as those obtained from operating theatres and endoscopy centres, for real-time review by remote specialist clinicians.
According to mobile operator HKT, its 5G network is able to support speeds of over 1Gbps with latency of less than 10ms. Such connections are fast and responsive enough to support very high quality 4K video, 3D imaging, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR) and multi-camera views, thereby providing a fully immersive experience for remote clinicians and students.
In Hong Kong, CUHK Medical Centre (CUHKMC) is using HKT’s high throughput and low latency 5G to support innovative medical applications, such as remote consultation, remote training, telemedicine, and treatments guided by AR services. HKT has built full 5G coverage across the entire CUHKMC hospital. Wholly owned by The Chinese University of Hong Kong, CUHKMC has 28 operating rooms, 49 consultation rooms and 516 beds for in-patients.
CUHKMC is using 5G technology to speed up consultation, diagnosis and treatment. In cases where patients need specialist advice and help, front-line medics have historically referred them to an expert in the relevant field of medicine. Such referrals can take time to arrange, delaying treatment. Since June 2021, CUHKMC has been using 5G to enable real-time remote consultation with specialists, eliminating the need for a separate appointment. An on-site doctor can promptly seek a second opinion from a remote specialist, thereby speeding up critical decision-making.
“Through the innovative use of 5G technology to support a wide array of smart hospital applications such as remote consultation (doctor-to-doctor), remote training (doctor-to-student) and telemedicine (doctor-to-patient), resources in the hospital can be optimised and patients can receive the best possible care,” explains Tom Chan, Managing Director of Commercial Group of HKT. “5G also supports other innovative applications such as the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) and robotics to better serve the Hong Kong public.”
Sources
- 1. https://windeurope.org/intelligence-platform/product/wind-energy-digitalisation-towards-2030/
03
Supporting surgery and follow-up consultations
CUHKMC operating theatres are fully covered with 5G, which is used to transmit multiple 4K video streams of the surgery as well as images captured by medical equipment, such as an endoscope. Where appropriate, multiple video streams are combined into a single view to give the remote clinician an immersive experience of the surgery. Accessible on a mobile device or PC, these visuals can help the remote specialist provide expert opinion on the surgery or can be used to help train students watching in an auditorium.
As 5G is designed to provide high speed, low latency and high reliability connectivity, it is the best option to support mission-critical medical operations, according to HKT. “5G is in licensed bands with full control on traffic loading and radio management, which is in sharp contrast with Wi-Fi in unlicensed bands, shared use with public traffic via contention and radio interference from unexpected Wi-Fi devices,” the telco explains.
Leveraging 5G connectivity, CUHKMC can provide a virtual follow-up consultation for patients, reducing the need for them to revisit the hospital. The quality of diagnosis can be further improved by harnessing the IoMT. For example, a connected blood pressure monitor could track the progress of recovering patients, both in the hospital and after discharge.
04
Keeping staff and students connected
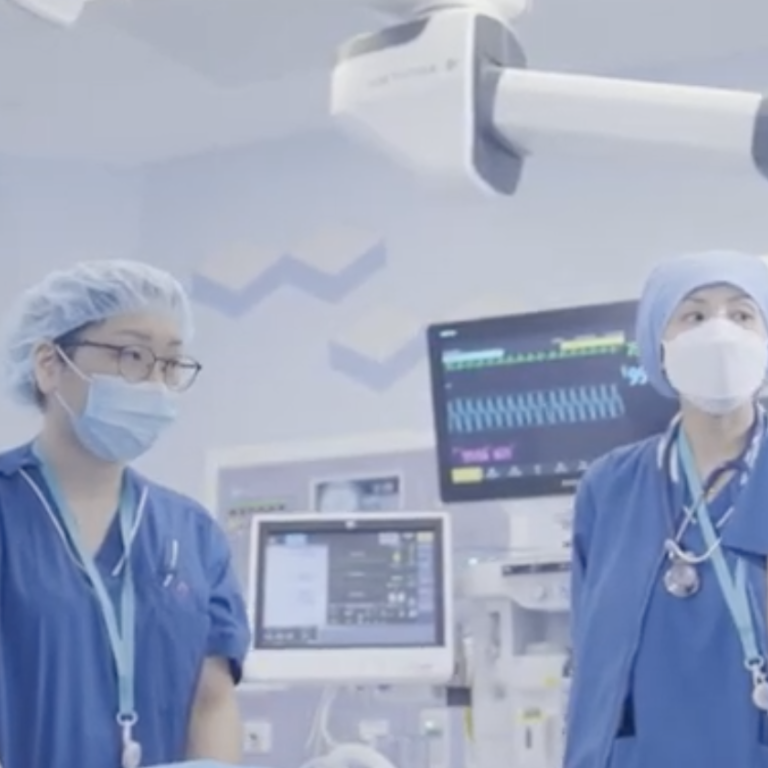
At the same time, the 5G network ensures reliable connectivity for CUHKMC staff and devices, such as cameras, iPads and medical equipment in operating theatres, endoscopy rooms, patient wards, and the multi-function auditorium, which is used as a training venue for broadcasting live streams of medical procedures. HKT says the 5G connectivity can deliver a seamless learning experience: the professor in the operating theatre can teach students in the auditorium as if they were in the theatre with him or her.
This approach means the hospital can train more than 20 medical students simultaneously in the auditorium. By contrast, when students had to be in the operating theatre in person, less than four students could watch the procedure. That equates to a fivefold efficiency improvement. Furthermore, the 5G connectivity enables the professors to ensure as many students as possible can view complex procedures performed on rare medical cases. “The opportunity of lecturing this rare case is valuable and it is important to maximize the benefit outcome with more students in the auditorium,” notes HKT.
In the face of the COVID-19 pandemic, 5G’s capacity for transmitting videos and images to the hospital auditorium and students’ mobile devices helps ensure the continuance of large-scale clinical training and seminars even during a pandemic outbreak.
HKT says the next step will be to elevate the use case from remote clinical training to support international conferences by extending the transmission from the local auditorium to multiple overseas hospitals. Looking to position itself as an international hub for medical excellence sharing, CUHKMC is connecting to renowned hospitals around the world. The 5G system could enable it to broadcast high-definition footage of surgical processes to remote audiences, further strengthening the international standing of Hong Kong’s healthcare industry.

Sources
- 2. GWeC Global Wind report 2021
05
Harnessing AR in healthcare
5G infrastructure is also used to support very bandwidth-intensive applications, such as AR and VR services. Today, clinicians use two-dimensional multi-slice images, such as those from a CT scan, to make a diagnosis; in future, 5G could offer them a three-dimensional model of scan results.
Through a 5G-connected headset, such as a HoloLens, medics will be able to view a detailed 3D model of the scan from multiple angles. Even bi-directional communication between two HoloLens is possible, allowing clinicians to simultaneously view and annotate on the same 3D model. In clinical training, a 3D model can be a very useful tool for professors giving lectures to medical students.
CUHKMC is trialling the HoloLens to explore potential use cases by various medical specialists. It is also evaluating whether artificial intelligence can support the medical analysis of lung and cardiac CT scans. The goal is to improve the efficiency of diseases analysis, diagnosis, and pre-operative evaluation.
“The focus of our smart hospital is to improve the patient journey by delivering optimal treatment and enhancing medical safety,” said Dr. Fung Hong, Chief Executive Officer of CUHKMC. “Through our partnership with HKT on 5G technology and applications, the digital transformation of CUHKMC is accelerated, thus improving the overall effectiveness and efficiency of the hospital.”
06
About
About the GSMA
The GSMA is a global organisation unifying the mobile ecosystem to discover, develop and deliver innovation foundational to positive business environments and societal change. Our vision is to unlock the full power of connectivity so that people,
industry, and society thrive. Representing mobile operators and organisations across the mobile ecosystem and adjacent industries, the GSMA delivers for its members across three broad pillars: Connectivity for Good, Industry Services and Solutions, and Outreach. This activity includes advancing policy, tackling today’s biggest societal challenges, underpinning the technology and interoperability that make mobile work, and providing the world’s largest platform to convene the mobile ecosystem at the MWC and M360 series of events.
For more information, please visit the GSMA corporate website at www.gsma.com.
Follow the GSMA on Twitter: @GSMA.
GSMA 5G Transformation Hub
The GSMA 5G Transformation Hub is a source of information on some of the most innovative 5G solutions in the world. This portal contains case studies detailing design, benefits, key players, measured value and the future impact of scaling up these 5G solutions worldwide. The 5G Era is now firmly established and this family of standardised GSM technologies, including mmWave, are being rolled out successfully across the globe. The GSMA 5G Transformation Hub, launched at MWC Barcelona in 2022, provides details of how 5G is best placed to deliver real value for a range of key sectors including manufacturing, energy, transportation, media and live entertainment, smart cities and construction.. Many more case studies will be added, in the coming months, covering even more industries and the GSMA is asking Members to nominate innovative 5G case studies to add to this global digital showcase. The 5G Transformation Hub and this particular Case Study are both sponsored by Qualcomm.
About this case study
This case study is for information only and is provided as is. The GSM Association makes no representations and gives no warranties or undertakings (express or implied) with respect to the study and does not accept any responsibility for , and hereby disclaims any liability for the accuracy or completeness or timeliness of the information contained in this document. Any use of the study is at the users own risk and the user assumes liability for any third party claims associated with such use.