5G Transformation Hub
How Private 5G Networks Can Optimise Vehicle Manufacturing
Private 5G network optimises business process
The Ford Motor Company uses a 5G mobile private network (MPN) in its’ research facility based in Essex, UK. The MPN team has implemented real-time process analysis and control of machines using 5G to continuously optimise vehicle manufacturing processes and enhance production efficiency.
Select a project
Contents
Challenge
Automotive parts need to be manufactured efficiently to tight tolerances so any variation in the repetitive process of assembling parts affects the quality of the output and any downtime costs money. Therefore, maintenance optimisation to identify and replace parts before they fail and eliminate unnecessary downtime needs to be supported by ultra-reliable connectivity. Low latency is required to enable the factory to react quickly so that settings on machines can be changed in milliseconds to continuously optimise production quality.
Solution
Ford and Vodafone trialled a 5G MPN-based connectivity solution at Ford’s e-drive pilot manufacturing facility in Dunton, Essex, UK. The solution harnessed 5G connectivity for multiple solutions including real-time analysis of machine performance and managing responses to changing conditions during the production process. Artificial intelligence (AI) based predictive maintenance was deployed to spot defects and reduce downtime and augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR) techniques were used to support remote maintenance of factory equipment.
Impact & Statistics
By deploying a 5G MPN, Ford was able to reconfigure their Dunton facility without the need to change ‘miles’ of physical cables, allowing for significantly cheaper and quicker deployment of new technology-enabled solutions. As the approach is adopted within Ford, the company will be able to bring new facilities online faster and enable manufacturers of production line machines to configure those machines remotely before deployment into Ford facilities, further accelerating commissioning time.
Wider Implications
Ultra-reliable 5G connectivity could play a fundamental role in enabling the manufacturing sector to adopt Industry 4.0 principles including very high levels of quality, automation, customisation and flexibility. A 5G MPN system has the potential to enable manufacturers to reconfigure factory floors, to make more efficient use of space and time, and optimise operational processes to drive cost savings and quality improvements.
Stakeholders
ATS Global, Digital Catapult, Ford Motor Company, HSSMI, Lancaster University, TM Forum, The Welding Institute (TWI), Vacuum Furnace Engineering,, Vodafone.
02
How Private 5G Networks Can Optimise Vehicle Manufacturing
Private 5G network optimises business process
In an intensely competitive economy, factories can’t afford any downtime. That makes ultra-reliable systems a must in manufacturing.
Deployment of a new private 5G network in a Ford Motor Company plant in Dunton, Essex, UK, points to how 5G can be sufficiently reliable to support crucial production and maintenance processes. Using connectivity supplied by Vodafone and co-funding from the UK government, the project ran over two years starting 2020. It had two physical test beds with one located at Ford’s e-drive pilot manufacturing facility in Essex, UK and another at TWI’s Research Institute in Cambridge, UK, both covered by a single MPN.
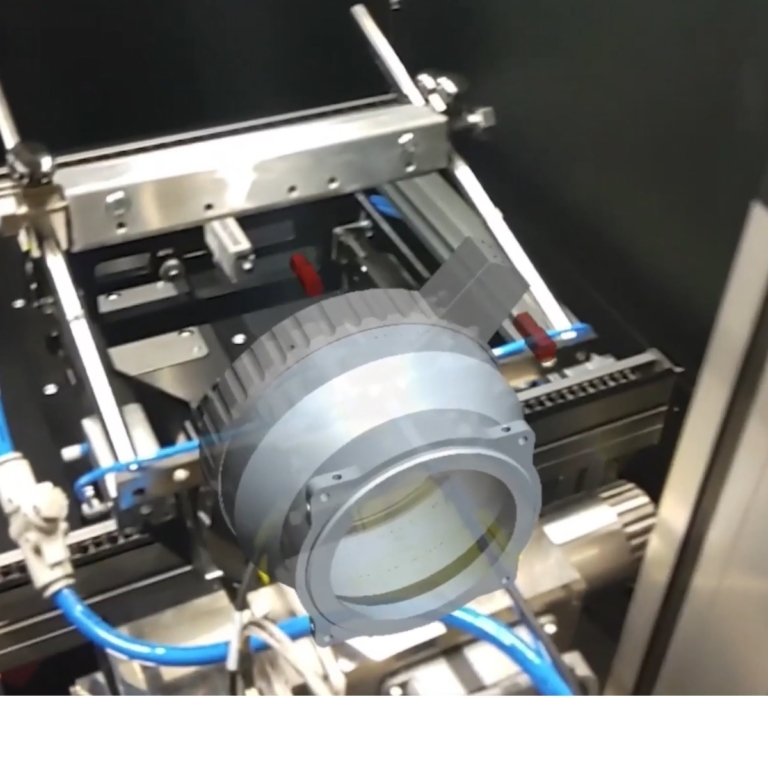
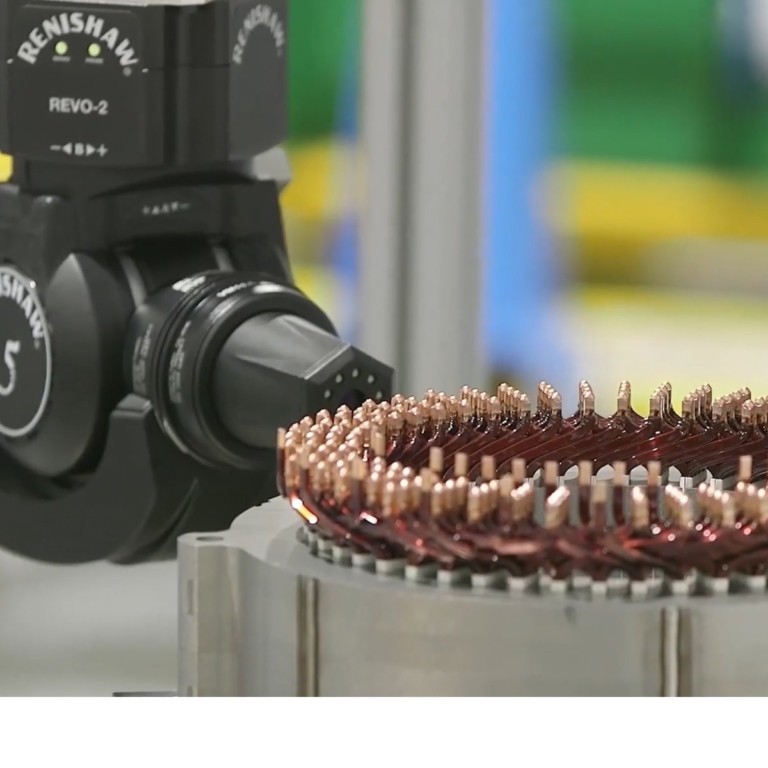
As part of the solution, a private 5G network is used to remotely control machines and monitor changing machine configurations. The MPN enables Ford to capture data from sensors installed throughout its electric vehicle factory in Essex. The 5G connected sensors were initially used for real-time monitoring and control of laser welding for hairpin joining in electric vehicles (EVs) and battery-bus-bar joining. Using the 5G network, Ford creates digital twins of its processes, then the factory team of on-site engineers and remote experts at The Welding Institute (TWI) in Cambridge collaborate to monitor the welding process. The process includes checking 192 welds per part at least 3 times per cycle and each time the machine processes data within milliseconds. To do that, TWI needs access to “many gigabytes of information,” notes Chris Allen, Senior Laser Welding Engineer, TWI. “5G enables those kinds of large volumes of data to be moved around with greater ease.”
This helps the firm in monitoring the complete production process and making automatic adjustments in response to changes in input materials, environmental conditions, and other factors. To optimise the vehicle manufacturing process, the laser welding machines must capture large amounts of data generated by the machine. “As manufacturing the motor and battery of an electric vehicle requires around 1,000 welds, the welding process can generate up to 500,000 pieces of data per minute.” explains Chris White, Ford’s 5GEM project lead. “The welding machines generate very high amounts of heat to fuse pieces of copper together and therefore make a perfect circuit. As we do that, we collect data to make sure that we know your car is perfect and won’t have any issues. That data is incredibly important to us and that’s why 5G is critical going forward.”
“Project partner ATS Global is capitalising on the speed of the 5G network to deliver a hybrid cloud directly to the shopfloor. The platform allows the consortium partners to deploy AI at the network edge, enabling robotic process automation to automatically carry out, repeat and improve processes.” says White. At the same time, high speed, reliable, connectivity enables Ford’s equipment suppliers to use AR and VR headsets to provide the automaker with remote support and assist with testing new configurations.
The private 5G network, which has its own 5G core, uses mid-range 1GHz – 6GHz spectrum provided by Vodafone, gives Ford control over provisioning and administration processes, such as activating/deactivating SIM cards. The technology is ideal for providing connectivity in manufacturing facilities, which previously would have been supported by ‘miles’ of physical cabling. “Connecting today’s shop floor requires significant time and investment,” concludes White. “Present technology can be the limiting factor in reconfiguring and deploying next-gen manufacturing systems. 5G presents the opportunity to transform the speed of launch and flexibility of present manufacturing facilities, moving us towards tomorrow’s plants connected to remote expert support and artificial intelligence.”

Chris White
Ford’s 5GEM project lead
03
Potential to reduce labour and efforts
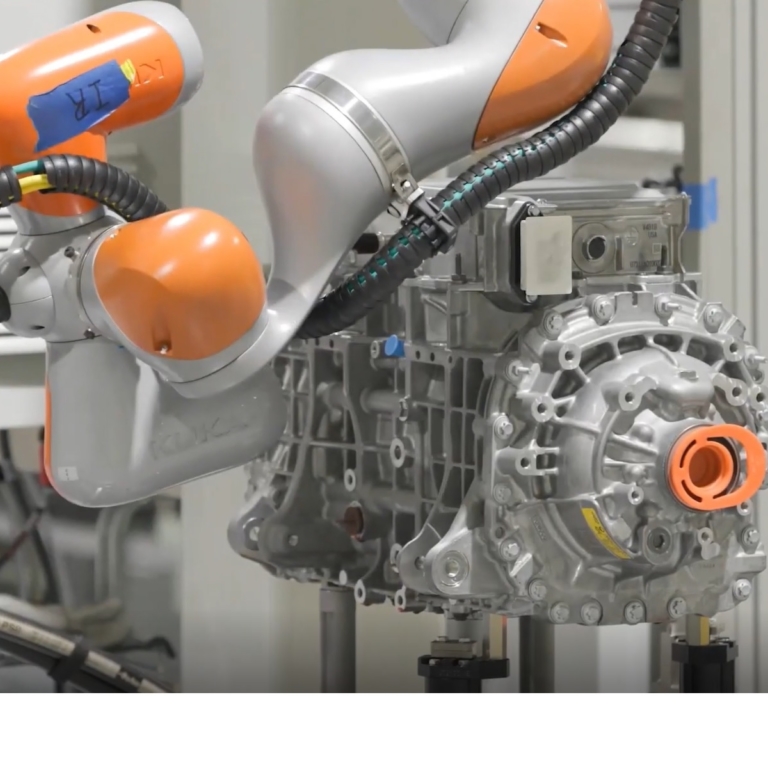
Ford Motors has used laser welding technology for EV manufacturing for a while, although the equipment did not have sensors onboard. Quality checking tasks were expensive, tedious and repetitive for the employees in the Ford factory. The firm wanted to explore ways for continuous monitoring and maintenance by connecting these machines to process the data.
The firm initially used 5G-connected sensors to monitor laser welding for hairpin joining and battery-bus-bar joining, supporting real-time control using data analytics and transferring the data from the welding machine via the 5G MPN.
“Using 5G to connect sensors wirelessly is ideal because of key 5G characteristics like high data throughput, low latency and the ability to connect with remote experts at TWI in Cambridge, where another 5G Mobile Private Network is also installed.”, says White.
The integration between Operational Technology (OT) and Information Technology (IT) worlds was extremely important for Ford but getting raw data out of the machines was a challenge involving data translation and mapping to new protocols that could be supported by the new IT environment. The solution was to use a particular gateway to assist with translation.
With the deployment of a dual campus 5G MPN and 5G enabled maintenance assistance, Ford managed to provide fast data sharing and connect its shop floor engineers with remote experts at TWI. One of the significant benefits enabled by the 5G MPN is the ability to change the settings on welding machines within milliseconds to continuously optimise production quality at full scale production volumes within factories.
04
5G combines flexibility, reliability and security
Ideally, manufacturing plants need the reliability and responsiveness of a wired connection and the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of wireless connections.
With a 5G MPN, they can potentially have the best of both worlds. Published in July 2020, 3GPP Release 16 introduced new capabilities to 5G, such as enhanced ultra-reliable low latency communication (eURLLC) with millisecond latencies, 99.9999% reliability, and Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) support. 5G also enhances security by allowing Ford to use SIMs on all its devices to ensure continuous monitoring of its dedicated network and protect it from external threats.
. With a private 5G network, there is little risk of interference from other wireless users. “With the project we are monitoring the manufacturing of vehicle electrical components through sensors attached to the manufacturing machines. We are also processing the data from those machines in real time to determine if we need to change settings to improve quality.” says White.
In collaboration with Vodafone, the project was executed in two phases. The first part of the project focussed on building the network to support more efficient laser welding processes, and the second on building a use case around maintenance.
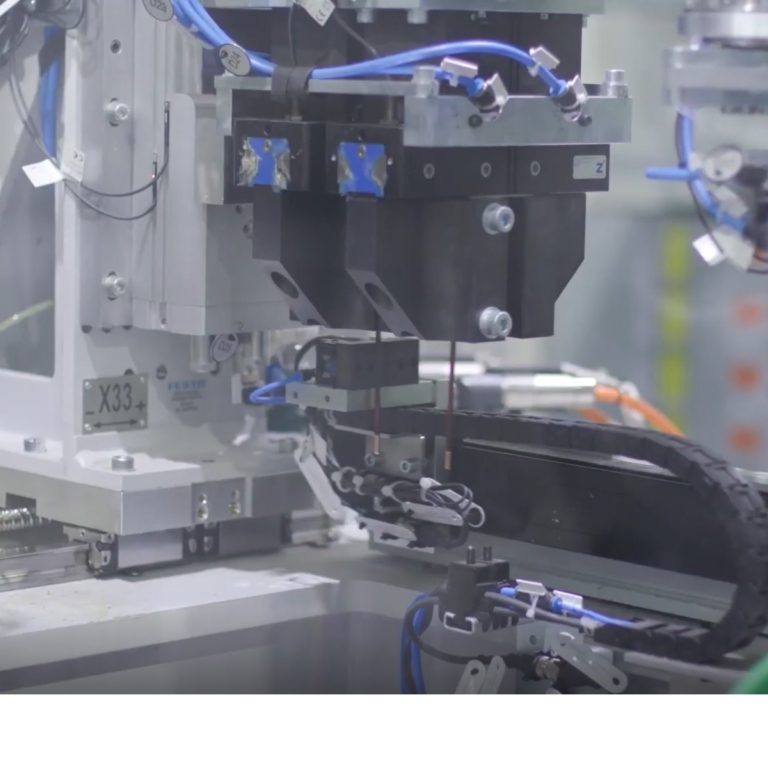
In the second phase, Ford deployed guided maintenance in a mixed reality solution using the PTC Vuforia platform. Data collected during the laser welding process allows automatic identification of any build-up of heat in the laser system. Typically, heat build-up means that the laser lens needs cleaning or replacing, and this maintenance activity can be automatically triggered. Wearing the HoloLens, a maintenance technician is then guided through the laser lens replacement process. Thus, the 5G MPN was useful in elimination of unnecessary downtime in the production line and consequent delays in manufacturing.
Ford used the HoloLens system to get real-time support from 5G-connected experts to diagnose and fix any problems using secure network access solutions and a secure gateway. This could be with experts at the TWI facilities in Cambridge, UK advising on laser welding issues or equipment manufacturers regarding issues on their machines
The hybrid cloud facility that was deployed as part of the solution incorporated local edge computing and was useful in processing a large volume of data. “The network is also integrated with a cloud computing environment where the data is stored, processed and shared with other consortium partners in the project.” said White.

Chris White
Ford’s 5GEM project lead
05
Next Steps - In conversation for upgrading its other facilities over the period 2023-2024
The Vodafone and Ford use case has run for two years. This not only involved testing the new technologies, but the test system is now live and is being used by Ford to demonstrate the potential of 5G MPNs and other new technologies in a realistic manufacturing environment.
As part of their next steps, Ford will focus on bringing together an ecosystem to support the deployment of private 5G networks in their other manufacturing facilities. The firm is in conversation with Vodafone to incorporate support for the deployment of private networks 5G in Spanish, South African and German facilities. “We have a non-standalone network, and of course standalone networks are now becoming available with advantages such as lower end-to-end latency – this loops back to the types of sensors and devices that will work in the facility. From a global perspective there are differences in how spectrum is going to be managed, and this will drive complexity for Ford if we want a global solution.” adds White.
In such cases, Ford may choose to use 5G mm Wave, which can support very fast throughput over short distances.
Another potentially interesting feature for manufacturing is ranging – the use of 5G signals to create a dense three-dimensional map of what is happening in a specific location. This feature could be used to create so-called digital twins of a plant or factory or to recreate the facility in the Metaverse. These solutions could be used to monitor the performance of the plant and detect any anomalies, such as a security breach, as well as running “what if” simulations.

06
About
About the GSMA
The GSMA is a global organisation unifying the mobile ecosystem to discover, develop and deliver innovation foundational to positive business environments and societal change. Our vision is to unlock the full power of connectivity so that people,
industry, and society thrive. Representing mobile operators and organisations across the mobile ecosystem and adjacent industries, the GSMA delivers for its members across three broad pillars: Connectivity for Good, Industry Services and Solutions, and Outreach. This activity includes advancing policy, tackling today’s biggest societal challenges, underpinning the technology and interoperability that make mobile work, and providing the world’s largest platform to convene the mobile ecosystem at the MWC and M360 series of events.
For more information, please visit the GSMA corporate website at www.gsma.com.
Follow the GSMA on Twitter: @GSMA.
GSMA 5G Transformation Hub
The GSMA 5G Transformation Hub is a source of information on some of the most innovative 5G solutions in the world. This portal contains case studies detailing design, benefits, key players, measured value and the future impact of scaling up these 5G solutions worldwide. The 5G Era is now firmly established and this family of standardised GSM technologies, including mmWave, are being rolled out successfully across the globe. The GSMA 5G Transformation Hub, launched at MWC Barcelona in 2022, provides details of how 5G is best placed to deliver real value for a range of key sectors including manufacturing, energy, transportation, media and live entertainment, smart cities and construction.. Many more case studies will be added, in the coming months, covering even more industries and the GSMA is asking Members to nominate innovative 5G case studies to add to this global digital showcase. The 5G Transformation Hub is sponsored by Qualcomm.
About this case study
This case study is for information only and is provided as is. The GSM Association makes no representations and gives no warranties or undertakings (express or implied) with respect to the study and does not accept any responsibility for , and hereby disclaims any liability for the accuracy or completeness or timeliness of the information contained in this document. Any use of the study is at the users own risk and the user assumes liability for any third party claims associated with such use.