The GSM Association (“Association”) makes no representation, warranty or undertaking (express or implied) with respect to and does not accept any responsibility for, and hereby disclaims liability for the accuracy or completeness or timeliness of the information contained in this document.
SKT Tango: AI-assisted Network Operation System
The case study centres on the potential of network automation enabled by AI (Artificial Intelligence). With the complexity of networks increasing in the 5G era, SKT developed an AI-assisted network operations support system, TANGO, which consolidates network management into one platform and enables better customer satisfaction.
Login above to view cost reduction figures.
TANGO stands for Telco Advanced Next-Generation OSS and is the total unified OSS (operations support system) platform for SKT’s mobile network. The main strength of TANGO is that it provides powerful data analytics and optimised automation based on AI capabilities in real-time. The power of TANGO is manifested in its various applications, such as 3D modelling to assist Radio Access Network (RAN) planning and automatic load balancing that optimises the RAN. In addition to TANGO’s potential in reducing the OPEX associated with network management tools, TANGO also provides the ability to expose an operator’s capability to 3rd party via Open API. This enables operators to monetise its network, especially for B2B customers. Furthermore, TANGO can be optimised for the operator’s culture and institution. OSS is not only a management or support system but an embodiment of the operator’s corporate culture and institution, making TANGO more attractive. With its experience in developing TANGO, SKT believes that it has moved closer to the goal of genuinely centralised network management platform indispensable for success in the 5G era. TANGO enabled a unified operating system that consolidates layered and silo-ed multiple OSSs, realising the efficiency of network management. Also, advanced analytics helped TANGO achieve better network management. For example, AI analytics will increase the decision with high speed, find hidden problems and analyse them automatically. Lastly, TANGO’s capability exposure benefits not only the operators but also the customers. The case of SKT and its unified OSS TANGO demonstrates the importance of AI analytics and consolidated OSS in realising the promises of 5G. As networks evolve through 4.5G to 5G with more complexity, network densification and intelligence at the edge, the need will be even more significant to automate network and a corresponding increase in cost (CapEx and OpEx).
1. Introduction
SKT (SK Telecom) is a leader in the mobile communications market in the Republic of Korea with more than 40% market share. With its dominance in the mobile communications market, SKT has pioneered to hone its technological competence by proactively innovating and deploying the latest technologies. For example, it was the first in the world to implement LTE Advanced Pro in 2017 and LTE Advanced in 2013. In the era of 5G mobile communications and industry transformation, SKT foresaw the potential of artificial intelligence in its network operations. Not only will artificial intelligence enable new service opportunities that were not feasible previously, but also will it optimise and simplify the network operations. In this context, SKT launched an advanced network operations support system (OSS) TANGO in October 2017. SKT developed TANGO by consolidating multiple legacy OSSs and empowering AI analytics into a cost-effective single platform. This case study describes TANGO and analyses SKT’s experience in developing and deploying the solution. The economic potential of TANGO for a typical operator will also be evaluated using GSMA’s Network Economics Model. Read more at www.sktelecom.com
2. Business Imperative
In the dynamic world of business, it is challenging for a company (let alone mobile operators) to keep up with the pace of change in its markets and technologies. AI is a technology that enables companies to automatically adapt to the changing environment and focus on identifying new business opportunities. In the mobile communications context, this is not restricted to the optimisation of network operations but encompasses the enhancement of customer experience and new revenue opportunities. AI is, therefore, an attractive technology for mobile operators, where they have to identify and develop new business models while mitigating the cost burden associated with network densification in the 5G era. For example, AI can enable automation of network operation and improve the performance of the network leading to zero-touch operation and cost burden reduction. Furthermore, discovering insight hidden behind multiple layers of complexity and creation of new patterns will enable better customer experience and new business opportunities. Indeed, the introduction of 5G brings more challenges to SKT, where it is managing four generations (2G ~ 5G) of networks as of July 2019 (decommissioning of 2G is planned for the end of 2019). Managing four generations of networks, along with IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem), increases the complexity of network management, not only impacting the cost but also performance. Another challenge in the 5G era is the introduction of dynamic network slicing, which requires on-demand real-time management of network slices to tailor the customer experience. Consequently, data analytics is needed inevitably to provide service satisfaction to the customers and key insights to SKT’s network management. Finally, planning of 5G radio base stations and configuration of coexisting LTE & 5G networks require a different paradigm of network management. AI and various use cases are expected to help SKT successfully address these challenges. In this context, AI is an indispensable component of SKT’s network in that it not only improves the economics of the network, but it also comes with other benefits. For example, the new revenue opportunities and customer satisfaction enabled by AI will be more prominent than cost reduction potential. While this case study will focus on the impact of AI solution on network economics; it will also describe other benefits qualitatively.
3. TANGO
TANGO stands for Telco Advanced Next-Generation OSS and is the total unified operations support system platform for SKT’s mobile network. The TANGO consists of six modules: Operation, Inventory, Engineering & Construction, Analytics, Data Warehouse and Platforms for unified OSS (see Figure 1).
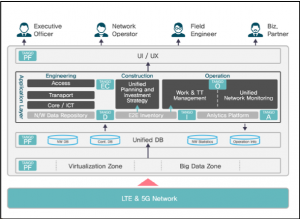
Figure 1. TANGO overview
The platform module spans three different layers. The first platform module leverages and collects data from SKT’s virtualised mobile network (4G & 5G) while processing the data into appropriate formats using SKT’s big data capabilities. The data is then processed and analysed into the second platform module, Unified DB (Database), where different databases (e.g., network statistics and operations information) can be accessed by both network OSS applications and other platform modules. The final platform module is the UI/UX (User Interface / User Experience) of other TANGO modules that provide the network OSS applications on top of the first two platform modules. Operation module provides network monitoring functionality for operation. The monitoring is not done for an isolated part of the network but in a unified manner. It monitors access network, transport network, core network, interoperability testing and virtualised network function to ensure that end-to-end macroscopic overview is possible. Inventory module possesses the end-to-end inventory of network resources (in both physical and logical layers) that enable management of end-to-end topology. Engineering & construction module allows an operator to manage planning and investment of the network from access, transport and to core networks. Analytics module brings in network big data end-to-end analytics for customer experience management. This module also interacts with Unified DB platform module. Finally, data warehouse module provides big data repository, data discovery and interfaces with Unified DB platform module.
3.1 Role of AI Analytics and Possible Use Cases
The main strength of TANGO is that it provides powerful data analytics and optimised automation based on AI capabilities in real-time. The real-time AI analytics process is as described in Figure 2. Firstly, the data from different parts of the network (radio access, backhaul/fronthaul and core) are correlated in data streams. The data streams then are analysed in parallel, where machine learning algorithms are applied. The machine learning algorithms enable anomaly detection to trigger automatic optimisation in the operation and maintenance of the networks by controlling different parameters and resources.
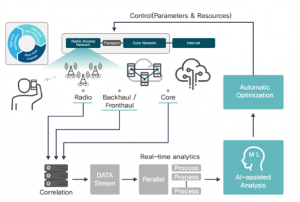
Figure 2. Analytics process of TANGO
More specifically, the AI analytics process is a virtuous cycle of the HCI (Human-Computer Interaction) agent, accumulated experience and business insights/inferences that AI analytics platform learns (see Figure 3). First, HCI agent, based on its prior cognitive learning, provides knowledge data to the particular issue that needs to be solved. The real-life experience in solving the data then is recorded in the unstructured DB platform which provides business insight to the AI analytics platform. The platform provides its learning into relevant TANGO modules, where the modules by its automation and analytics capability provide inference/suggestion to the HCI agent.
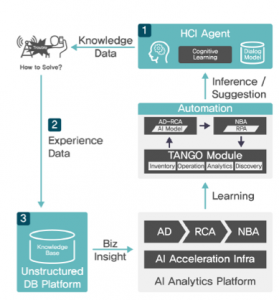
Figure 3. The virtuous cycle of AI analytics
AI analytics, reinforced by its virtuous cycle and characterised by superior analytics capabilities, opens up myriads of use cases that TANGO can offer. An example, depicted in Figure 4, where RAN base stations can be optimised considering E2E experience of the customer. First, the base stations can be optimised by balancing the load among different spectrum bands. In the times with low demand, the base stations or different spectrum bands can be selectively turned off, optimising the utilisation of the asset. During congestion, the turned-off base stations or bands can be turned on again to address the increase in demand.
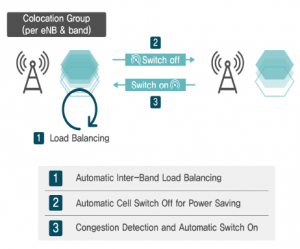
Figure 4. RAN Base Station optimisation
TANGO also supports 3D modelling that significantly reduces the difficulties associated with planning 5G radio (for both below and above 6GHz band). The tool enables the mobile operator to model the coverage in both outdoor and indoor settings in 3D (see Figure 5). Based on the modelling, the AI and machine learning functions recommend 5G sites as shown in Figure 6.
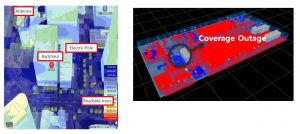
Figure 5. Outdoor (left) and indoor (right) 3D simulation of 5G radio
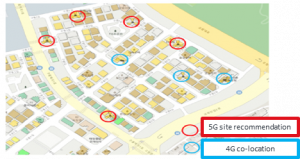
Figure 6. Recommendation of 5G sites
Interested readers are encouraged to read Table 1, which contains more AI use cases that TANGO can offer.
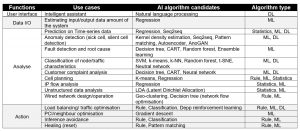
Table 1. Example use cases of TANGO
4. Economic Benefits
This section highlights the benefits that TANGO can deliver to mobile operators. The first subsection focuses on the quantitative cost reduction enabled by TANGO. The last two paragraphs qualitatively describe the optimisation of customer experience and TANGO’s ability to fit into a mobile operator.
4.1 Network Management Tool Cost
The immediate cost-benefit to the mobile operator is that the cost associated with network management tool is reduced. Resources for TANGO both of CAPEX and OPEX are planned to achieve ROI (Return of Interest) in the first five years for adopting the unified network management tool and 40% cost reduction is expected after five years compared to the total cost of operating legacy OSSs. Relying on a single network equipment vendor can create lock-in for mobile operators where adding a functionality/feature may not be feasible or economically while switching from a vendor to another may be extremely challenging. Bearing in mind such difficulty, many operators pursue a multi-vendor approach to establish their networks. Meaning that purchasing network management tool license for different network components would be immense. Furthermore, the tools would be silo and would not interwork well with other vendors tools. In this perspective, TANGO has the potential to realise further savings in the costs associated with network management tools, which consequently would reduce OPEX.
4.2 Customer Experience Optimisation
TANGO can also optimise the experience of mobile operator’s customers with its powerful analytics and optimisation capabilities. For example, it can analyse the traffic congestion of different areas in a real-time manner and over a specific period. Enabling the mobile operator to focus its resource on traffic congestion areas and apply load-balancing mechanisms to smoothen the traffic distribution. In addition to optimisation, TANGO exposes its capability to 3rd party via Open API. As shown in Figure 7, the B2B customers of network slice can access the OSS to monitor quality & utilisation and to gain insights from the data intelligence. The customers can use the data and the analytics insight to optimise its services.
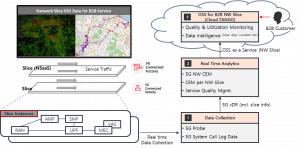
Figure 7a. OSS analytics for network slice customers
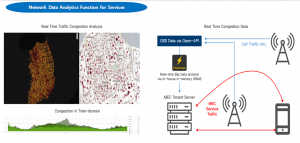
Figure 7b. OSS analytics for network slice customers
An example of capability exposure would be where tenants in the MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) will have more opportunities in optimising service quality in their applications (see Figure 8).
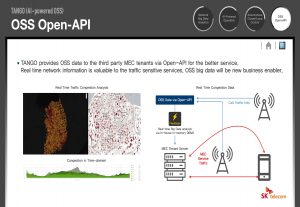
Figure 8. MEC and TANGO’s Open API
4.3 Operator-optimised Solution
Optimisation to a particular operator is the key strength of TANGO. OSS is not merely a management or support system, but an embodiment of the operator’s corporate culture and institution. While other network management tools are fixed and focused on the target network component; TANGO can be implemented and adapted in a way that is optimised to the operator’s corporate culture. Taking into account that many innovations have failed uptake because of a discrepancy in the corporate culture, an innovation that can be adapted into a corporates culture promises operators that TANGO can be taken and exploited to the fullest of its potential.
5. Lessons learned
With TANGO, SKT witnessed openness and standardisation are highly required for telco-driven data collection, network analytics, and network optimisation. For the operation of 5G network, which was initially debuted in December 2018 for the smart factory as B2B service and on the 3rd of April 2019 for B2C, SKT enabled TANGO for the 5G service. This section lists lessons learned from SKT’s experience.
5.1 Background
With 5G network, SKT expects intelligent connectivity between massive devices will be available with ultra-reliable low latency and enhanced broadband. However, in perspective of network operation, there are challenges in the management of 5G network. Though the architecture of 5G network is much simplified compared with the legacy network, increased number of radio cells will be a significant burden to the operator. Estimations on the amount of radio cell will be at least 2.5 times of the present with a minimum assumption of same coverage of SKT’s LTE network. Also, the stability of 5G and 4G networks should be guaranteed simultaneously for the operation of 5G NSA (non-standalone) network since NSA network depends on the 4G network for its signal flows in control-plane (i.e. master node is 4G). After total migration of 5G from NSA to SA (standalone), nevertheless, telco should manage heterogeneous legacy networks such as 3G and 4G to satisfy the service requirement of various handset types. Customers’ expectation toward 5G will require more operational efforts. Conventionally, to manage and to operate the telecommunication network, various kinds of OSS are required from end-to-end points of all generations of network. The network operator needs specific multiple OSSs to manage physical NEs (network elements) located in all domains of radio access, transport, and core network. For example, SKT had more than 150 OSSs before consolidation into TANGO. Also, VNF (virtual network function) that runs on one or more VMs (virtual machines) on top of network infra is another NE to be managed and monitored for its stable operation. For the mission-critical services with massive IoT devices, the network will be sliced logically based on the service requirement in the 5G era. Sliced networks should also be managed and guaranteed to satisfy minimum service quality for their special purpose. Clearly, for this high standard of hybrid network operation, ZSM (Zero touch network and Service Management) is required. However, the conventional method of management will require overheads in the process of a complex network; hence operational transformation with intelligence and efficiency is indispensable in 5G network operation.
5.2 Truly Unified Network Management
SKT’s experience in developing TANGO provides some hint to achieving truly unified network management platform.
5.2.1 Unified Operating System
Most importantly, a unified operating system is necessary to increase the efficiency of network management. It is recommended that layered and silo-ed multiple OSSs should be consolidated into a cost-effective single platform by integrating key modules to operate the hybrid / heterogeneous network from end-to-end. With this single OSS platform, for example, network slices for a different quality of service (QoS) should be managed and quickly assured from the phase of creation to termination. Avoiding confusion and obstacles caused by many redundant and silo solutions in network orchestration. With the OSS platform, assurance of regular operation of all networks including physical, virtual, and sliced network can be achieved, and service satisfaction will be obtained by managing customer experience as agreed in service level agreement.
5.2.2 AI Analytics
Advanced AI analytics should be running on the OSS with real-time network data, and manual and routine jobs powered with AI analytics. The outcomes of AI analytics can increase the decision with high speed, find hidden problems and analyse them automatically. AI can be applied in a distributed or a centralised way over the OSS or the network, and its use cases can be the heart of network automation for closed-loop control such as anomaly detection, root cause analysis, predictive prevention, network healing, optimisation. Also, the telco should be re-organised to operate the network with the AI-based OSS. The goal is zero-touch network operation, achieved by preventing human errors via AI analytics use cases.
5.2.3 Capabilities Exposure
Outcomes of network analytics should be exposed to players in telco eco-systems and even to Over The Top (OTT) service providers. Network analytics data is valuable not only to the operator but also to the contents providers for their best quality service delivery amid demanding requirement. For instance, location-based traffic congestion can be informed to any application servers positioned in MEC and the traffic can be optimised more accurately. Also, an analysis of customers’ experience is useful in the marketing side or in discovering new business. The data is accessed via a subscription and is the same way the NWDAF (NetWork Data Analytics Function) is standardised in 3GPP, where the related work is currently on-going. 5G OSS including network analytics will lead to improved customer-centric services, and enable monetisation with the new application.
6. Conclusion
The operation of a 5G network can be a challenge for telecommunication companies, despite from the significant investment required in the network, mobile operators will be able to find new opportunities with the unified OSS platform based on AI analytics which can orchestrate the entire network more efficiently. Operation efficiency can be obtained with the platform, and the monetisation of use cases by leveraging the platform from B2C to B2B services in an agile way. AI-based network analytics, network as a service (NaaS), and OSS as a service (OaaS) will be useful assets for the discovery of new use cases to be monetised.
Login above to view cost reduction figures
