Building on insights discussed in last year’s article – 5G in Central and Eastern Europe: Poland Still Waits for True 5G While Bulgaria Sprints Ahead – we’ve reviewed 5G progress in the region again this year in terms of spectrum allocation, 5G performance as well spectrum refarming. Read on to learn more about 5G progress in Central and Eastern Europe.
Key takeaways
- Late 5G Spectrum Allocation in Poland: While Poland was the last country in the region to allocate dedicated 5G spectrum, it has now initiated an auction for the crucial C band (3400-3800 MHz) to catch up with its neighbors.
- Spectrum Refarming to aid 5G rollout: Many countries in the region are repurposing mid-band spectrum and shutting down 3G networks to allocate spectrum for 4G and 5G services.
- North Macedonia leads on 5G Performance: North Macedonia had the highest median 5G download speed in the region, and its capital city (Skopje) was not only the fastest in the country, but it also ranked high in our global city speed rankings (25th).
Poland finally auctions 5G spectrum
When we last discussed the state of 5G across Europe, Poland was the only country in the region without dedicated 5G spectrum. At that time, all neighboring countries had already assigned C-band, and all bar Bulgaria were assigned low-band frequencies for 5G. There was limited interest in high-band (mmWave) frequencies, as we’ve witnessed in other parts of the world.
However, a notable shift occurred in May 2023 when Hungary’s National Media & Infocommunications Authority (NMHH) conducted an auction for 32 GHz frequency band spectrum because mmWave (24.5-26.5 GHz) is primarily used for fixed point-to-point and point-to-multipoint systems with some licenses set to expire in 2024 and the majority in 2027. NMHH intends for current users of the 26 GHz band to migrate to the 32 GHz band, making the 26 GHz band available for 5G use.
Below is an overview of the 5G spectrum status across select Central and Eastern European countries:
After a number of delays, Polish telecom regulator, the Office of Electronic Communications (UKE), began its auction for C-band spectrum (3400-3800 MHz). This is one of the crucial pioneer bands for 5G. All four Polish operators have submitted bids for 100 MHz blocks within the 3400-3800 MHz band at auction, which is expected to end by 11 November. Access to at least 100 MHz contiguous spectrum in C-band, the ITU’s minimum technical requirement to meet 5G performance requirements, will help Polish operators achieve faster speeds, lower latency, and improved spectral efficiency.
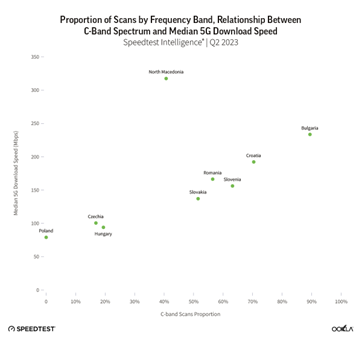
Furthermore, our research shows that countries using C-band spectrum (3 GHz – 6 GHz) for 5G experience faster download speeds than those on other bands. The chart below illustrates that this is the case in Central Eastern Europe as well. A higher proportion of scans on the C-band spectrum correlates with faster median 5G download speeds, as seen in countries like Bulgaria and Croatia. It’s worth noting that North Macedonia deviates from this pattern, which can be attributed to multiple factors, including Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS), the country’s size, and the concentration of coverage in its capital, Skopje.
Spectrum refarming to aid 5G deployment
According to our data, a significant amount of bandwidth used for 5G is through lower mid-band (1000 MHz to 2600 MHz). We have observed that most 5G services in Poland utilize lower mid-band spectrum, given that the country’s spectrum auction has not finished yet. Additionally, more than 40% of tests conducted in Czechia, North Macedonia, Slovakia, and Romania were on mid-band. In contrast, 70% of tests in Hungary were performed on low-band spectrum, which helps enhance coverage (but often at the tradeoff of slower speeds). For example, in May 2023, Magyar Telekom announced that it had increased its outdoor 5G coverage to 60% of the population by this summer as part of its mobile network modernization program, carried out over multiple years. Magyar Telekom provides 5G networks over 700 MHz, 2100 MHz, and 3600 MHz spectrum bands, with the current development typically switching on 5G at 700 MHz.
Mobile network operators are refarming mid-band spectrum to provide faster and more advanced 4G and 5G services. To make this happen, several operators across four countries have already shut down their 3G networks, with seven more operators in five countries planning to do the same. A1 Slovenija decided to switch off 3G mobile network services on June 30, following Telekom Slovenije, which ended its 3G services last autumn. Slovak Telekom also plans to shut down its 3G network this year and use the freed-up 3G bands for 5G services (it already uses some of its 2,100 MHz spectrum for 5G). Orange Slovakia announced in December 2022 that it plans to disconnect its 3G network within a year. In Poland, Orange will start sunsetting 3G in late September and complete the process in 2025. T-Mobile already began dismantling its 3G network in Poland in Q2 2022 and will shut down by year-end 2023. The operator plans to use the 900 MHz band released from its 3G sunset for LTE and 5G.
North Macedonia scores high on 5G performance
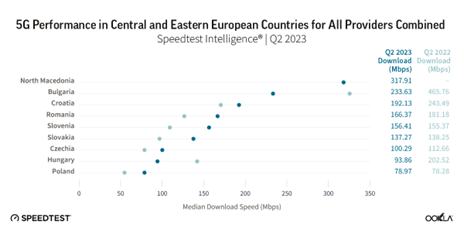
Our data shows that in Q2 2023, North Macedonia achieved the highest median 5G download speed in Central and Eastern Europe at 317.91 Mbps. Bulgaria was the only other country in the region that topped 200 Mbps (233.63 Mbps). It’s worth noting that North Macedonia not only excels in terms of median 5G speed but also when looking at 90th and 10th percentile results. For example, 5G download speeds in the 90th percentile reached 788.30 Mbps, while speeds in the 10th percentile clocked in at 90.90 Mbps. Makedonski Telekom and A1 Macedonia launched their 5G services with a combination of 4G frequencies using DSS before the 5G spectrum auction, with the regulator, AEK, awarding the licenses for frequencies in the 700 MHz and 3.6 GHz bands for 5G in July 2022. Makedonski Telekom invested over EUR 70 million in 2022 for network development.
While countries in the region continue to invest in 5G solutions, it’s worth noting that users could see 5G speeds decline after more and more users join and congestion ticks up.
Another factor contributing to the decrease is the need to adhere to coverage obligations, for which low band is better suited, resulting in lower median speeds.
A1 Bulgaria and Yettel Hungary head to head
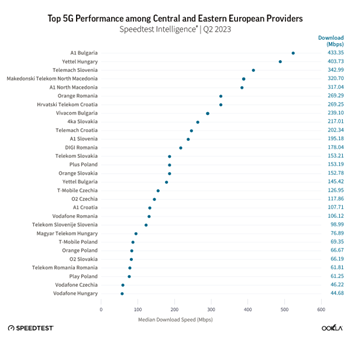
According to Speedtest Intelligence data, median 5G download speeds in different parts of the region can vary greatly. For instance, Vodafone Hungary had a speed of 44.68 Mbps, while A1 Bulgaria boasted a speed of 433.35 Mbps in Q2 2023. In most markets, our results show a clear 5G leader when it comes to speed, and A1 Bulgaria has emerged as that leader in Bulgaria.
In May 2023, Nokia announced a successful trial of Nokia 5G Standalone (SA) Cloud RAN in A1 Bulgaria’s commercial 5G network. This trial followed A1 Bulgaria’s 5G SA network integration in October 2022. The 5G SA network consists of a Radio Access Network (RAN) built with Nokia equipment and Ericsson’s dual-mode 5G Core backbone network. Meanwhile, the second fastest operator, Yettel Hungary has improved its 5G performance as well, with its median 5G download speed increasing from 349.61 Mbps in Q2 2022 to 403.73 Mbps in Q2 2023, while at the same time, Yettel Hungary reported that its 5G network coverage increased from 5% of the population in 2022 to 16% in 2023.
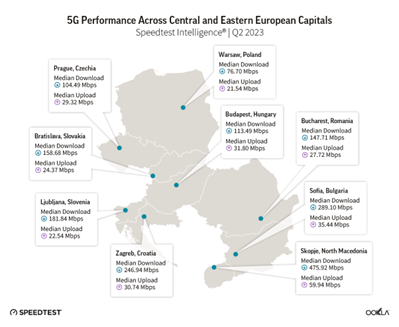
Skopje leads the pack
Map of 5G Performance Across Central and Eastern European Capitals
Given that North Macedonia had the fastest 5G among its peers, it isn’t surprising that its capital ranked first among regional capitals, with Skopje boasting a 475.92 Mbps median 5G download speed and a 59.94 5G upload speed in Q2 2023.
The conditions of 5G licenses for Macedonian operators state that by the end of 2023, at least one Macedonian city should be covered with a 5G signal. But it is not only 5G that is achieving good performance. Skopje also ranked 25th on our Global Index City Speeds in July 2023, with a median mobile download speed of 96.79 Mbps, placing the city just behind Sofia in our rankings but ahead of some Western European capitals like Paris, Amsterdam, Lisbon, Berlin, Rome, and London.
The Road Ahead for 5G in CEE
In Central and Eastern Europe, the progress and hurdles of 5G development are becoming more apparent. Poland’s decision to allocate C-band spectrum is a positive step forward. Other countries are still transitioning their networks and reallocating spectrum.
The sunsetting of 3G networks is a global trend. Leading mobile operators are sunsetting 3G to free up spectrum for newer technologies and move their customers onto faster technology. Ookla recently hosted a webinar sharing lessons learned on how to use crowdsourced network intelligence to address those challenges and the impact of repurposing 3G spectrum to more advanced technology. Some of the ways Ookla data can help is by identifying areas where either 2G or 3G signals are strong and where 4G LTE networks can be improved with network planning and optimization.
Ookla retains ownership of this article including all of the intellectual property rights, data, content graphs and analysis. This article may not be quoted, reproduced, distributed or published for any commercial purpose without prior consent. Members of the press and others using the findings in this article for non-commercial purposes are welcome to publicly share and link to report information with attribution to Ookla.