As part of our blog series. which focuses on the efforts of mobile operators in emerging markets to lead comprehensive e-waste management schemes, we spoke with Jutaphat Pitiphapada, from AIS, about their e-waste initiative and driving a sustainable business.
AIS is committed to conducting a sustainable business with consideration for economic, social and environmental aspects. AIS set seven strategic priorities for sustainable business, with long term aspirations and goals, under which there are two environmental priorities:
- Reducing GHG emission; and
- Managing waste properly.
Their goal for waste management, is to reduce and recycle waste from operations, as well as to encourage customers to dispose of e-waste properly.
AIS declared a key mission on improving the environmental quality of life for Thai citizens under the theme “Mission Green 2020”, campaigning for greater awareness of environmental issues and encouraging the public to drop off their e-waste at AIS shops under the project “Dispose of E–waste with AIS”. AIS volunteered to become a centre for the collection of e-waste from users, providing them convenience by allowing for the disposal of electronic products at all AIS shops across the nation. The AIS CSR team lead on the project and oversee all the operations to achieve the objectives and target.
What are the objectives/key KPIs and how much has been achieved so far?
 Objectives
Objectives
AIS, as the largest telecommunications service provider in Thailand and a major retailer of smartphones and electronic gadgets, acknowledges that taking part in the effort to protect the environment by reducing and recycling e-waste must be one of its missions. The company has committed to spreading awareness and knowledge to the Thai people about proper disposal of e-waste and made preparations to comply with forthcoming laws, such as the Electronic Appliance and Devices Disposal Act, which is expected to place the onus on business operators for terminating e-waste from products and services.
KPIs
AIS is aiming to collect three million pieces of e-waste by 2022. We have a plan to improve the covered areas across the country and to develop the collection process and transportation, which require safety considerations and better defined standards.
Performance
A full scale communication campaign was launched with a focus on building understanding among Thai people on the physical dangers of keeping expired e-waste at home and promoting knowledge on recycling and proper disposal. The goal was to have Thai people be more aware of the environmental threat e-waste poses, and persuade them to join in the effort to drop off e-waste with AIS. The total amount of e-waste received as of April 2020 is 45,931 pieces, which in turn, is equivalent to 459,310 kilograms of CO2 reduction.
Who are your key partners? And what role do they play?
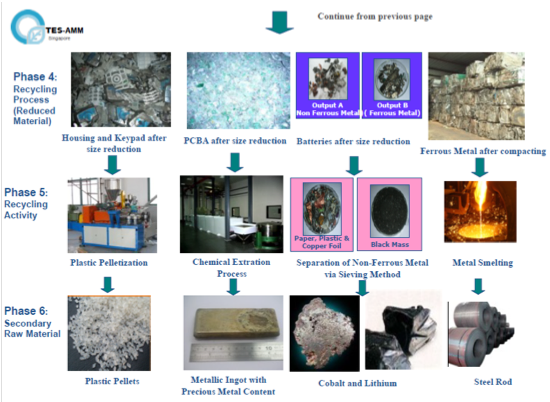
 Proper recycling process with TES
Proper recycling process with TES
TES, established since 2005, has become the global leader in providing information technology (IT) lifecycle services, offering solutions that help to manage the retirement of IT equipment with all local and international data security, environmental, and industry regulations.
AIS works with TES for e-waste recycling. All e-waste is forwarded to disposal facilities that adhere to international standards. Collected waste is then divided into two categories, recyclable and in need of termination. The factories report their operations back to AIS for evaluation and assurance that the undertaking is not adversely affecting the environment.


Safety and high standard of transportation with Thailand Post
Thailand Post is the main public postal service provider in Thailand, providing the full end-to-end logistic service including postal mail, parcel and money transfer service.
AIS partner with Thailand Post. Thailand Post collect all the e-waste across the country and forward to TES for correct recycling.
What is the user journey (for collections from customers)?
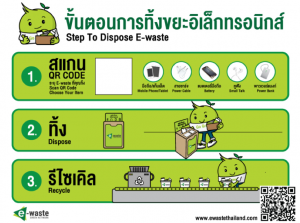 Customers can find the e-waste bins at AIS Shops and business partner places such as:
Customers can find the e-waste bins at AIS Shops and business partner places such as:
- Thailand post offices
- Universities
- Department stores
- Company partner office buildings
- Customer scans a QR code and enters the information about the type and amount of e-waste submitted for recycling
- AIS collects e-waste for forwarding
Find out more information about tracking the drop points and the e–waste journey
Is there a specific business model?
AIS truly aim to be the part of the environmental impact mitigation from its business operations and emphasises developing processes to reduce waste, increasing the recycling of waste and promoting that Thai people take part in properly disposing of e-waste. There is no any business model at this stage.
Do you involve any informal sector participation for this project? If yes, how?
As this project relates to hazardous waste, we focus on the collaboration between the certified organisations for the proper process and align with local laws.
What is required for further scale?
AIS plan to expand the project by partnering with both the public and private sectors (including universities, department stores, business partners) with the intent to promote awareness of the health and environmental dangers of substances that can leak out of e-waste if not properly disposed of. We also collaborate with “Thailand Responsible Business Network (TRBN)”, who were assembled under the “No Waste Vibhavadiee” program and engaged the member companies to participate the project. AIS also has plans to apply the project to certify the Thailand Carbon Offsetting Program (TCOP), which encourages the private sector and industrial sector of Thailand to demonstrate environmental responsibility by offsetting the organisational emissions. AIS aim to generate carbon credits from this project to apply in GHG reduction projects in Thailand.


